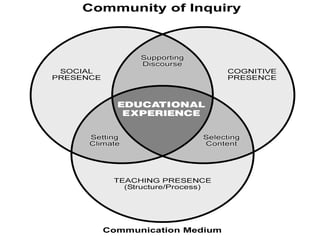
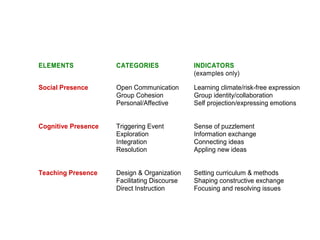
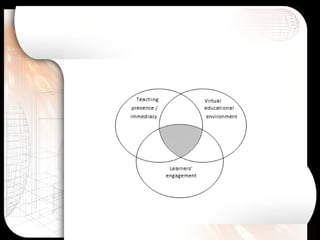
The document discusses the rise and significance of online learning, highlighting its growth in student enrollment and the shifting educational paradigms towards virtual environments. It emphasizes the importance of teaching presence and immediacy in online settings to enhance student engagement, satisfaction, and learning outcomes. The text also outlines challenges faced in transitioning from traditional classrooms to virtual learning spaces and the critical roles instructors play in fostering effective online education.