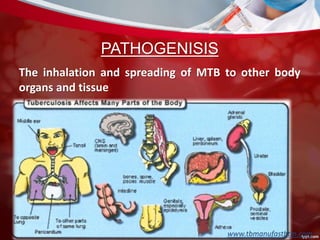
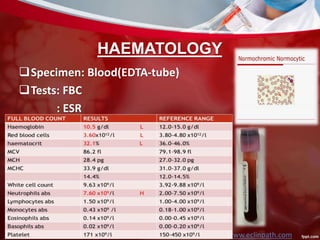
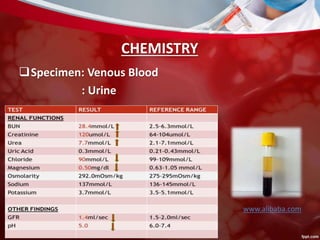
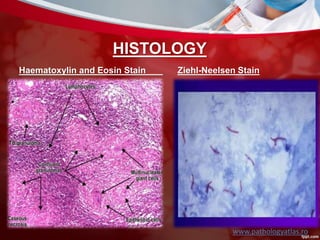
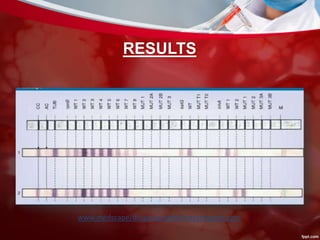
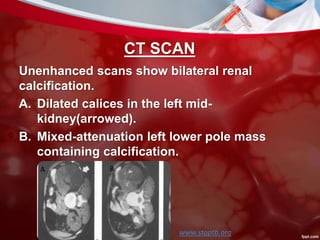
This document discusses non-pulmonary tuberculosis, specifically renal (kidney) tuberculosis. It outlines the risk factors, most common sites of infection, pathogenesis, signs and symptoms of renal TB. It then describes the laboratory diagnosis including hematology, chemistry, histology, microbiology tests and results. A case study is presented and diagnosed as renal TB based on positive acid fast bacilli staining, PCR, culture and histology findings. Risks, treatments, and references are also summarized.