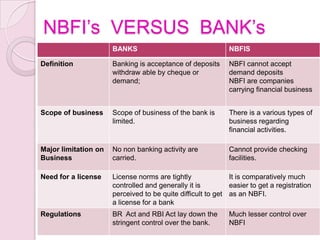
This document discusses non-banking financial institutions (NBFIs) in India. It defines NBFIs as financial institutions that provide banking services without a full banking license. It outlines key differences between NBFIs and banks, importance of NBFIs, functions of NBFIs like mobilizing savings and channeling funds, types of NBFIs including insurance companies and mutual funds, regulations NBFIs must follow, guidelines on fair practices, and top performing NBFIs in India like HDFC and Bajaj Finance.