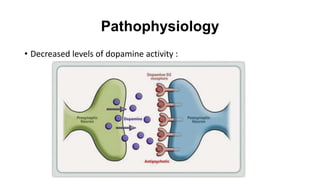
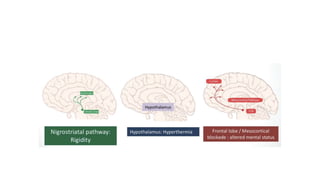
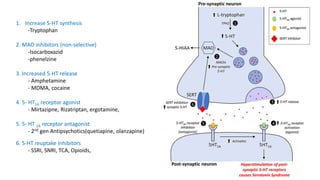
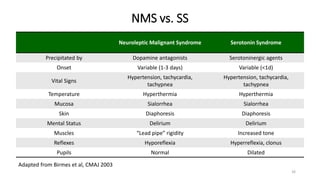
This document provides information on Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) and Serotonin Syndrome (SS). NMS is a life-threatening reaction caused by antipsychotic medications that results in altered mental status, muscle rigidity, fever, and autonomic dysfunction. It is associated with low dopamine activity in the brain. SS occurs due to excessive serotonin activity in the brain and body, usually caused by an interaction between two or more serotonergic drugs. The clinical presentation of NMS includes fever, muscle rigidity, delirium and autonomic instability while SS presents as cognitive/behavioral changes, autonomic dysfunction and neuromuscular abnormalities such as myoclonus. Both require discontinuing