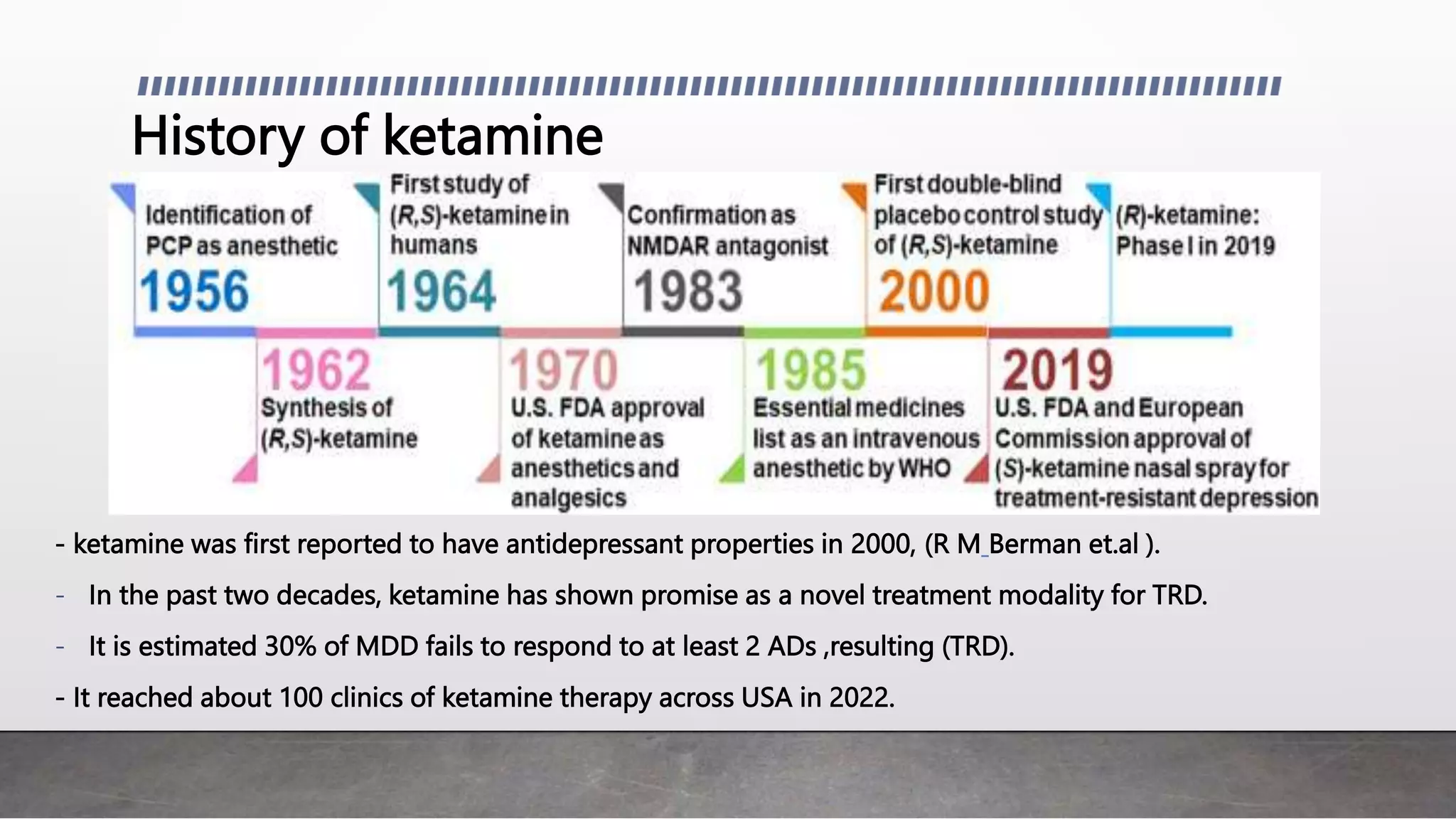
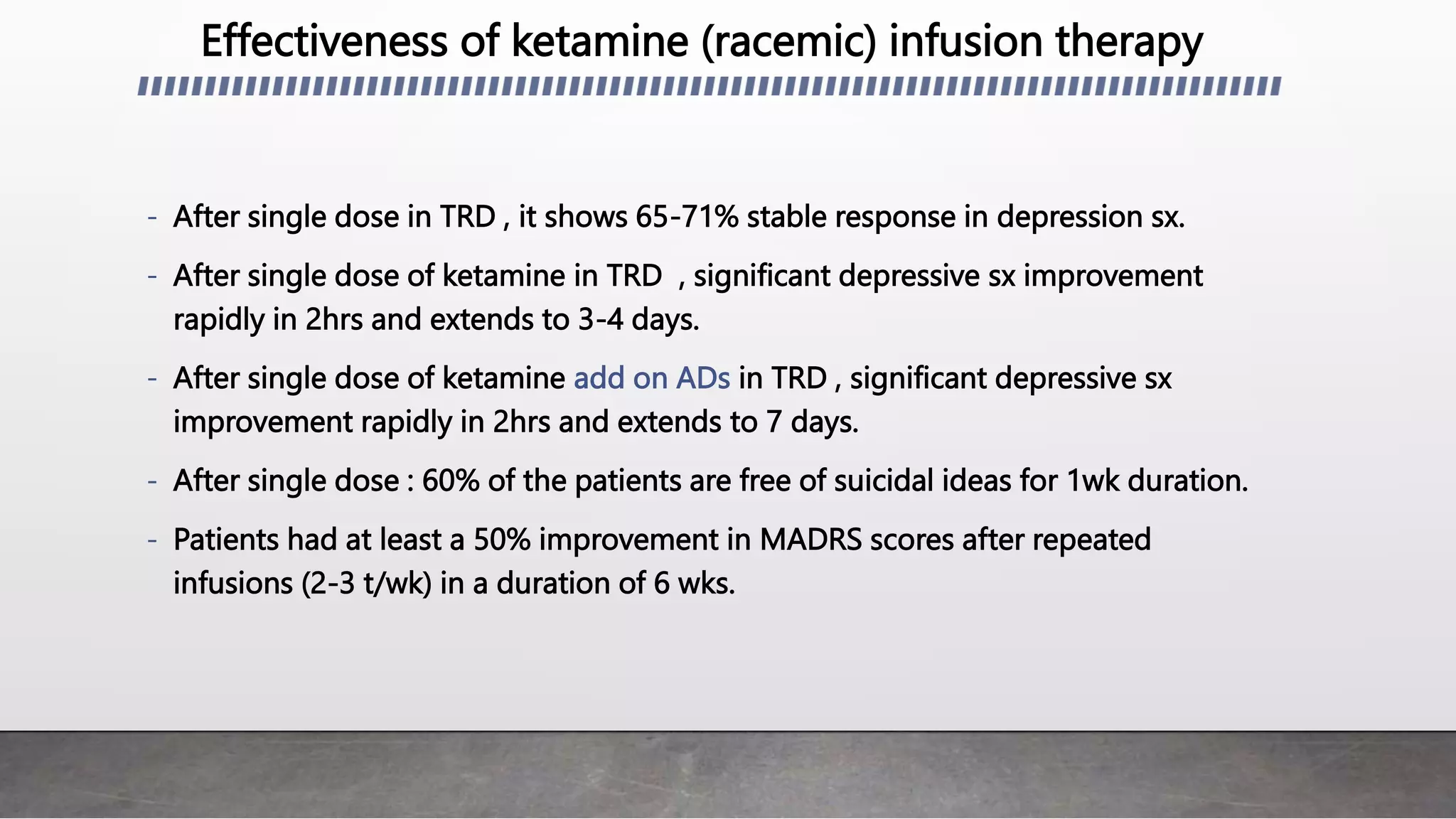
- Ketamine therapy shows promise for treatment-resistant depression (TRD). A single intravenous dose of ketamine can rapidly improve depressive symptoms within 2 hours for 3-4 days.
- Ketamine's mechanisms of action involve modulating the glutamatergic system and increasing neuroplasticity and neurogenesis. It may normalize brain connectivity and disrupt ruminative thinking.
- Intranasal esketamine received FDA approval for TRD and results in a 54.1% response rate and 36% remission rate with twice weekly dosing over 4 weeks. Ketamine infusion therapy also shows effectiveness for TRD.
- Common side effects include dizziness, dissociation, nausea, and increased blood