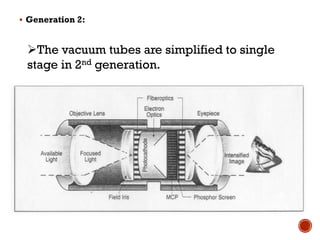
This document discusses night vision technology, including its working principles and applications. It describes two types of night vision - image intensifiers and thermal imaging. Image intensifiers work by amplifying available light so that more electrons are produced, creating a visible image. Thermal imaging detects infrared radiation emitted by all objects based on their temperature to generate images without visible light. The document also covers the four generations of night vision devices and their uses in military surveillance, wildlife observation, search and rescue operations, and security.