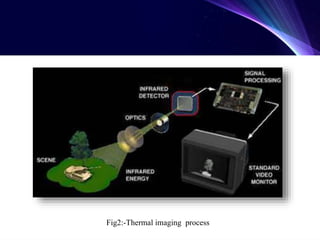
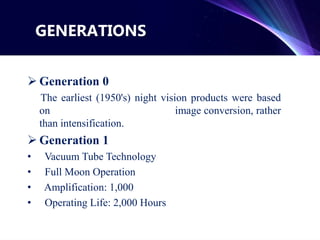
Night vision technology allows humans to see in the dark using either biological or technical methods. Technical night vision uses image intensifiers that amplify available light or thermal imaging that detects infrared radiation. Night vision devices include scopes, goggles, and cameras and have progressed through several generations with improved amplification and operating life. Key applications of night vision technology include military operations, hunting, security, and wildlife observation.