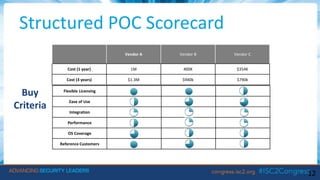
The document discusses next-generation endpoint solutions, highlighting their importance in combating prevalent threats like phishing and malware that predominantly target user endpoints. It outlines evaluation criteria for selecting such solutions, including multi-layered protection, cloud support, and integration capabilities, while also reviewing various vendors and their offerings. Additionally, the document emphasizes the necessity of adapting to evolving security needs and the significant financial backing of major players in the industry.