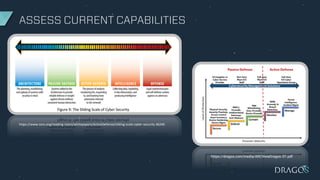
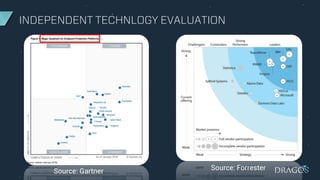
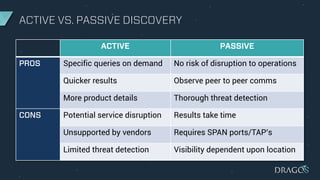
The document outlines criteria and considerations for selecting cybersecurity technology for Industrial Control Systems (ICS), emphasizing the need for threat detection and incident response capabilities. It discusses the importance of evaluating technology alongside existing systems and aligning requirements with organizational goals, while highlighting various technologies for asset discovery and threat management. Recommendations include establishing clear evaluation criteria and the significance of independent testing to assess solutions effectively.