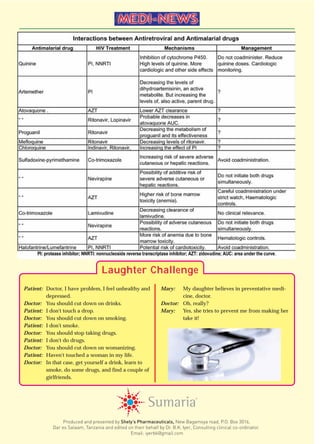
This document discusses the interactions between HIV and malaria. It begins by introducing the topic and noting that the high fever found in immunosuppressed HIV patients can lead to missed malaria diagnoses. Several studies are then summarized that show HIV negatively impacts the body's ability to develop immunity and produce antibodies against malaria. The document continues by discussing how malaria may increase HIV viral load and transmission risk. It notes that the greatest interaction occurs when one disease is highly prevalent and the other is low. The implications for treatment are that malaria must be diagnosed and treated in HIV patients to control viral load. In areas of high malaria and HIV, the diseases have less impact on mortality. Overall, the document examines the bidirectional relationship between the two diseases.