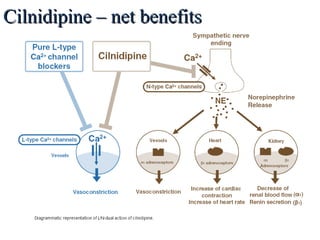
Cilnidipine is a dual-acting calcium channel blocker that blocks both L-type and N-type calcium channels. It is used to treat hypertension. Studies have shown that cilnidipine is as effective at lowering blood pressure as amlodipine, but it does not cause reflex tachycardia and has a lower risk of side effects like ankle edema. Combining cilnidipine with drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system provides improved blood pressure control and reduces cardiac remodeling compared to other calcium channel blockers. Cilnidipine's unique dual blocking properties also help regulate leptin secretion, reducing atherosclerosis risk in obese hypertensive patients