The document provides an overview of HIV and AIDS, including:
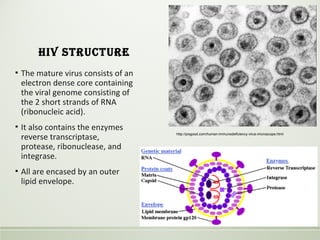
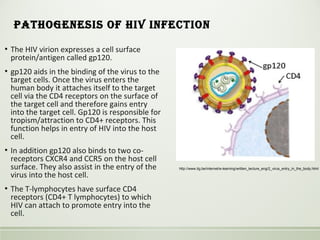
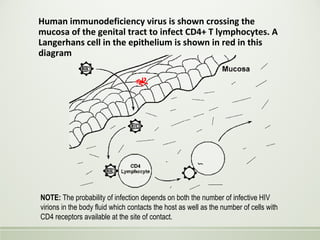
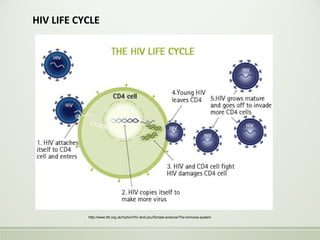
- HIV is a retrovirus that infects and destroys CD4+ T cells, ultimately leading to AIDS.
- Primary HIV infection may cause acute symptoms that resolve within months. Years later, very low CD4+ counts lead to opportunistic infections defining AIDS, like Pneumocystis pneumonia.
- Common infections include Pneumocystis jiroveci, CMV, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and fungal infections. Kaposi's sarcoma and lymphomas are associated cancers.