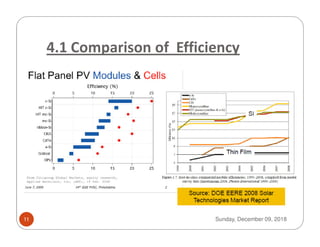
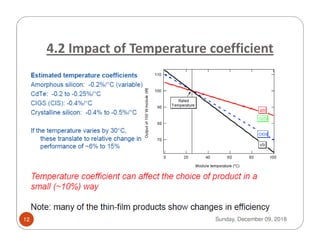
The document discusses new technologies in photovoltaic (PV) systems. It begins by explaining the basic working principle of PV cells and then classifies PV technologies into silicon and thin film categories. It describes the efficiencies of different cell types and emerging technologies that can achieve higher efficiencies. The document also addresses the impacts, economics, and future prospects of PV as well as scenarios in India and worldwide. It concludes by stating that quality PV components with long lifetimes are key and that the future of the technology is promising for supplying electricity and promoting development.