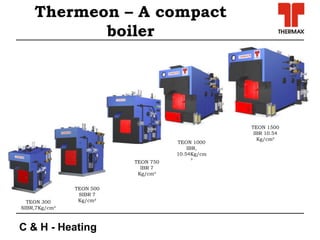
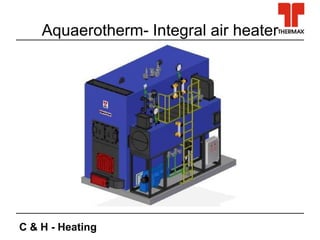
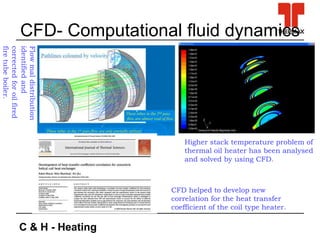
This document discusses new technologies in process heating. It covers combustion technologies for fossil fuels and biomass, as well as biomass boiler designs. Challenges in biomass combustion include low density fuel with high moisture and emissions. New combustion technologies aim to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and be compact and cost-effective. Computational tools like CFD and FEA are helping develop new products and solve design problems. Condensing technology allows recovering latent heat to boost efficiencies above 100%, but introduces material challenges.