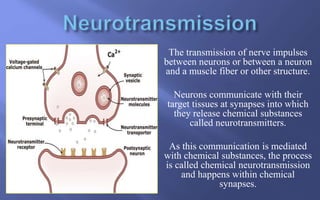
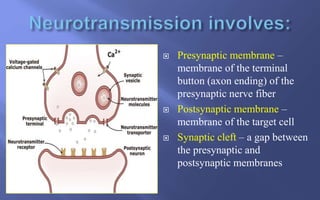
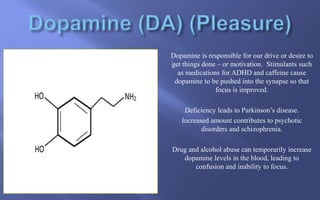
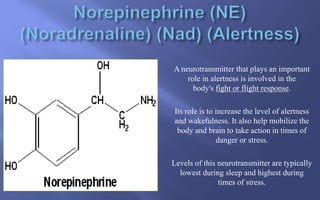
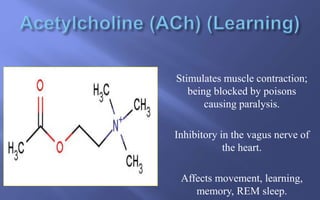
This document summarizes key aspects of neurotransmission. It defines neurotransmitters as chemical messengers that carry signals between neurons to control bodily functions. Neurons communicate at synapses by releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes. Neurotransmitters are either excitatory or inhibitory, with excitatory neurotransmitters triggering signals and inhibitory neurotransmitters blocking signals. Specific neurotransmitters discussed include serotonin, GABA, glutamate, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, histamine, and endorphins. Their roles and impacts on mood, behavior, learning, and other functions are described.