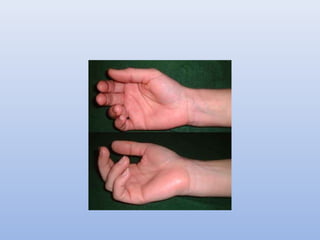
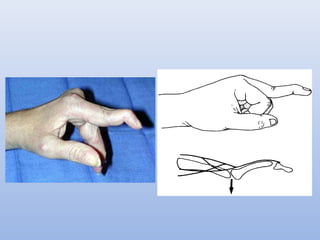
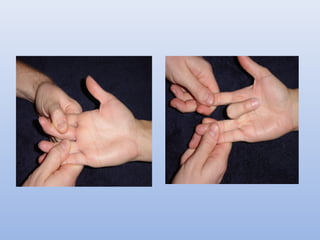
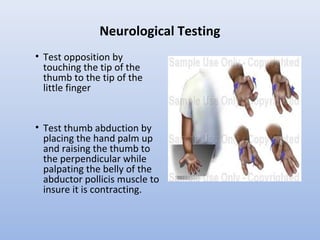
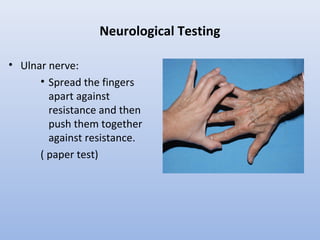
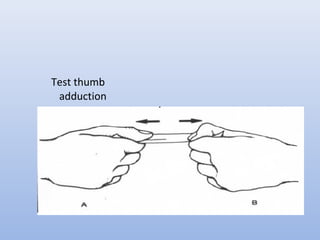
This document outlines the basic principles for examining the hand. It discusses obtaining a thorough history including injury details, medical history, occupation, and smoking status. The examination involves inspection for deformities, atrophy, swelling or scars. Palpation checks for warmth, dryness and assesses specific structures. Range of motion and muscle/tendon function are tested through active, passive, and resisted motion. Neurological testing evaluates sensory and motor function of the median, ulnar and radial nerves. Vascular assessment checks the pulse, color, temperature and capillary refill. Stability and special tests are also performed to check for specific injuries or conditions. A complete hand examination follows this systematic approach to thoroughly evaluate the structure, function