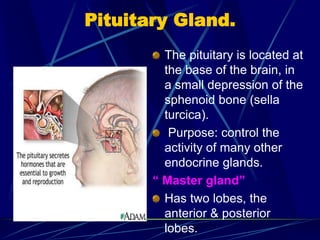
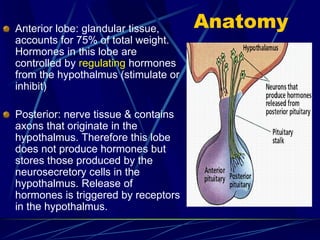
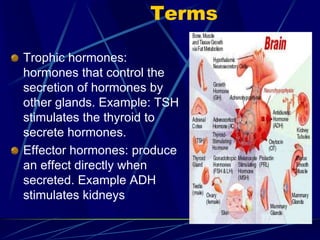
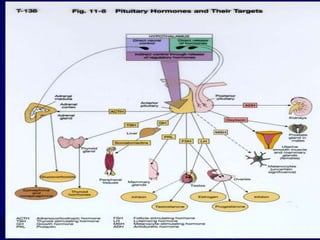
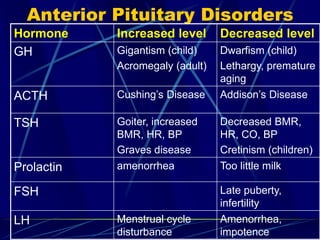
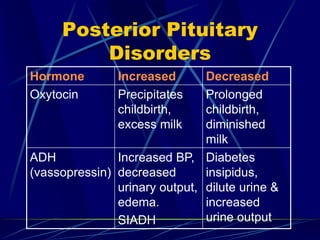
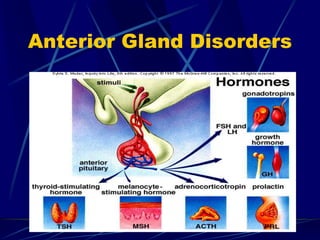
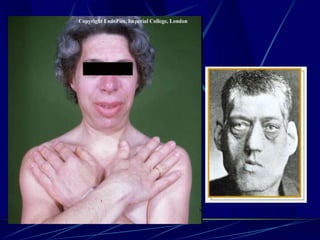
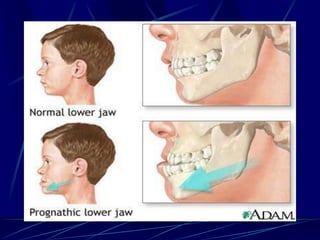
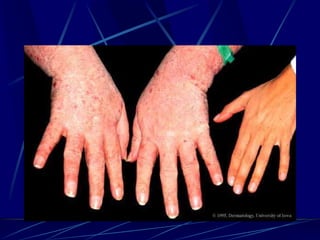
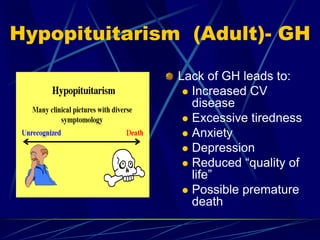
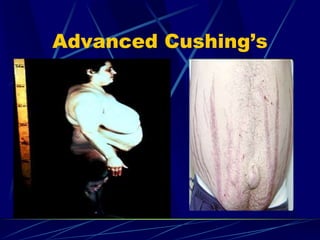
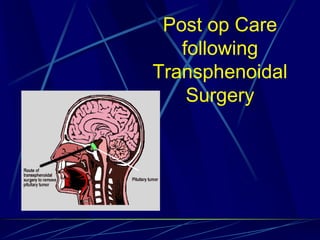
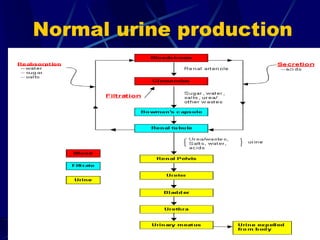
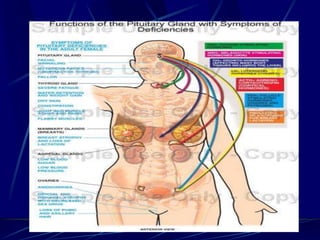
The document provides an overview of pituitary gland disorders, highlighting the functions of the anterior and posterior lobes and the hormones they produce. It discusses various conditions associated with hormone imbalances, such as hyperpituitarism, hypopituitarism, Cushing's disease, and diabetes insipidus, along with their symptoms, diagnostic processes, and treatment options. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of the pituitary gland in regulating endocrine functions and maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance.