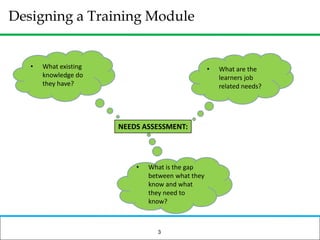
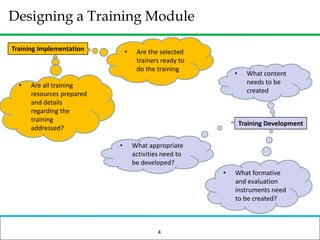
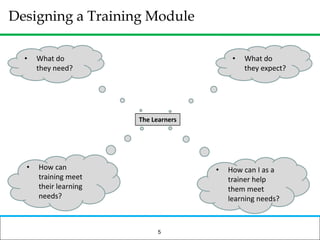
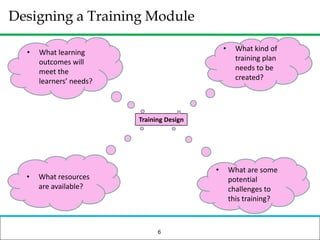
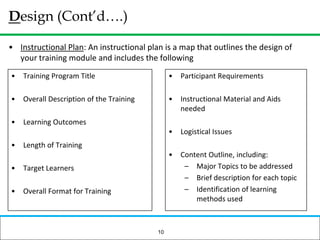
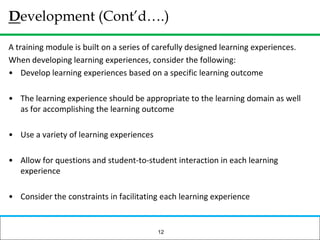
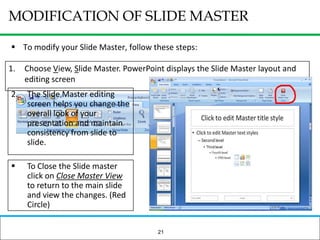
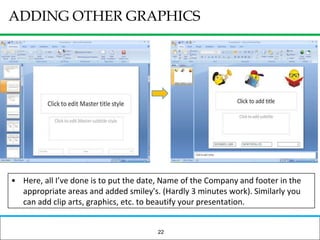
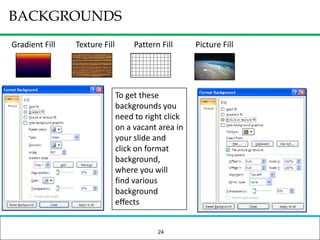
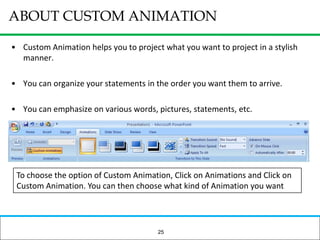
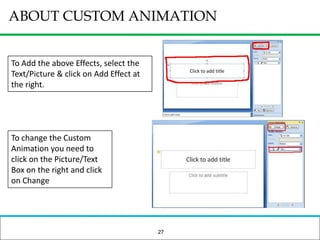
The document outlines how to prepare a basic training module, focusing on the ADDIE framework which includes assessment, design, development, implementation, and evaluation. It emphasizes the importance of understanding learners' needs, creating effective content, and developing engaging instructional materials while providing tips for designing PowerPoint presentations. Key elements discussed include needs assessment, instructional plans, activities, and the use of various training techniques to enhance the learning experience.