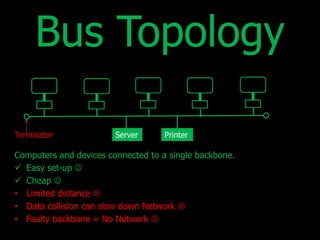
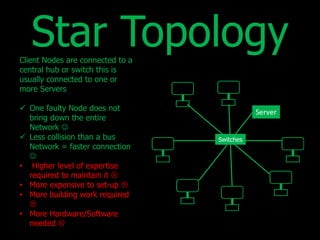
The document discusses different types of computer networks. A local area network (LAN) connects devices within a single location like a school or office, while a wide area network (WAN) connects LANs over a larger geographical area using public infrastructure like the Internet. A metropolitan area network (MAN) is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN, typically encompassing a city. Networks can be configured in different topologies like bus, star, ring, and peer-to-peer. They can also use different architectures like client-server, where a server provides resources to client devices, or peer-to-peer where devices have equal priority and share resources directly.