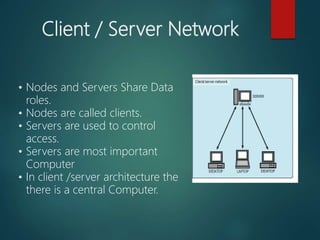
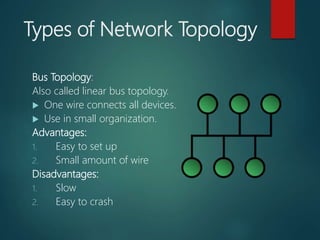
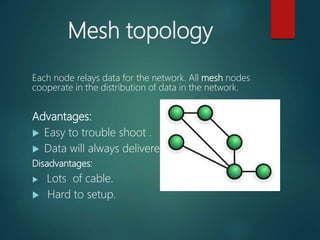
This document discusses computer networks and their types. It defines a computer network as a set of interconnected computers that share resources like internet access. The document outlines different types of networks including local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), wide area networks (WANs), personal area networks (PANs), client-server networks, and peer-to-peer networks. It also discusses various network topologies such as bus, star, ring, mesh and tree configurations.