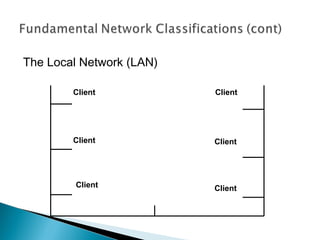
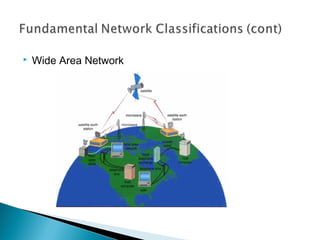
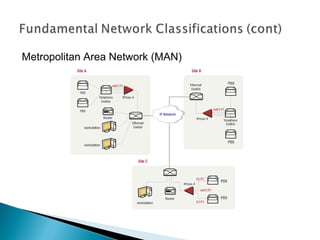
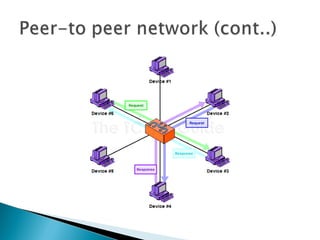
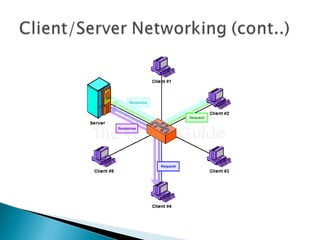
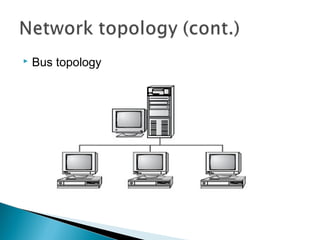
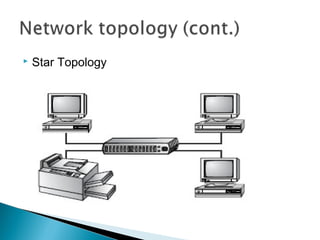
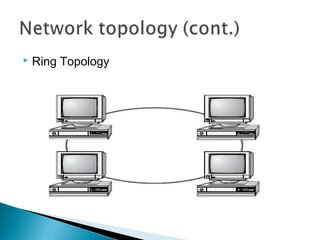
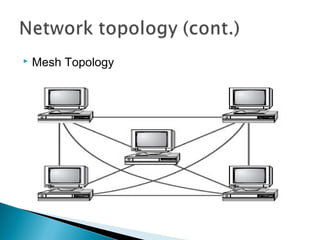
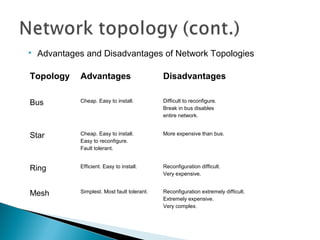
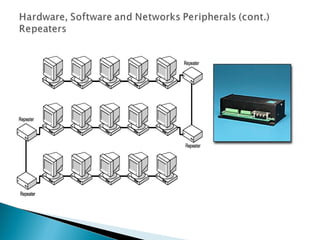
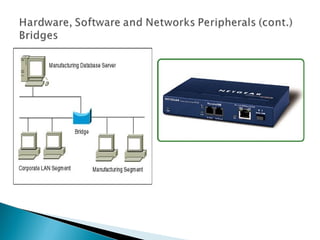
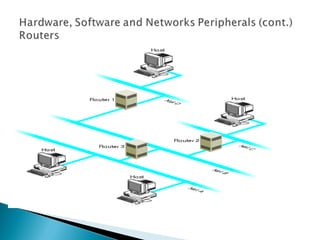
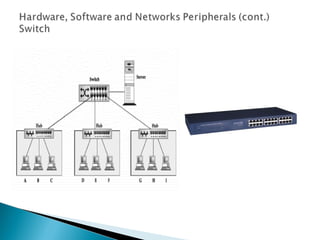
This document provides an introduction to computer networks. It defines what a network is and discusses the purpose of sharing resources between connected computers. It describes different network topologies including bus, star, ring and mesh and explains common network hardware like switches, routers, hubs and network interface cards. The document also distinguishes between local, wide and metropolitan area networks.