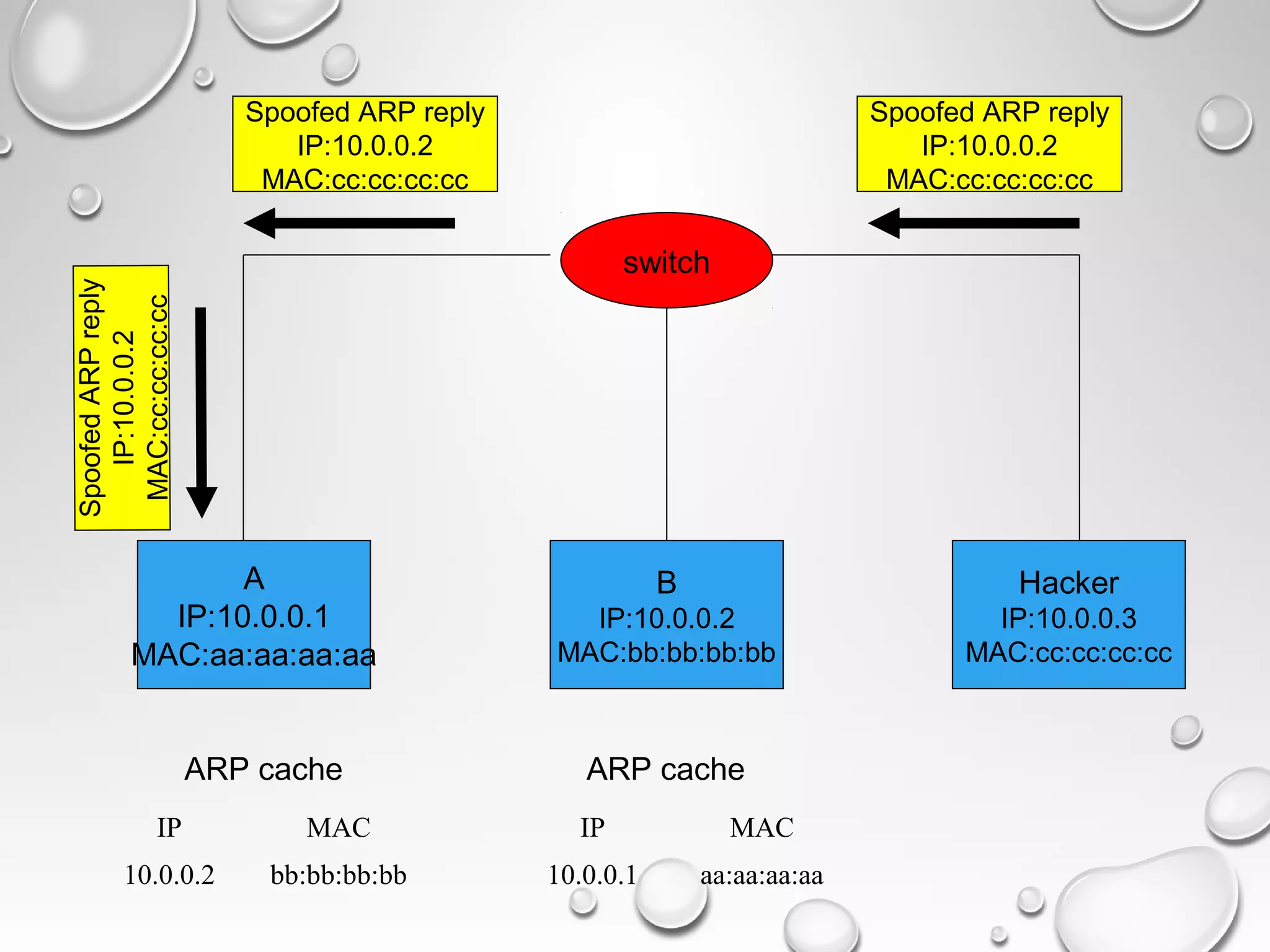
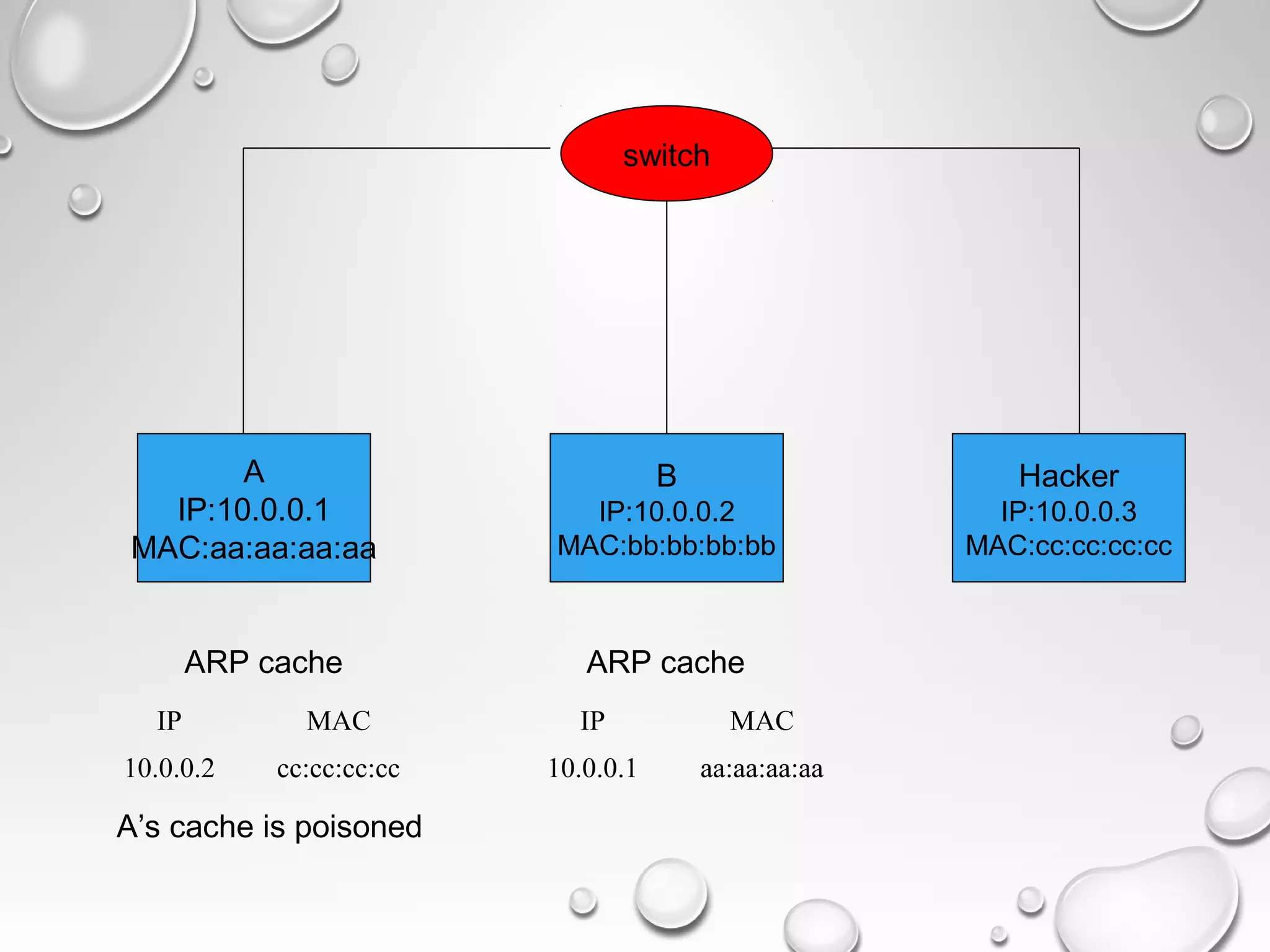
This document discusses ARP spoofing and poisoning techniques that can be used by hackers. It explains that computers have both a MAC address and IP address, and that ARP spoofing involves sending spoofed ARP replies to associate another computer's IP address with the hacker's MAC address, tricking the target into sending packets to the hacker. The document outlines how this works, possible attacks it enables like sniffing, and some defenses like static ARP entries. It also notes differences in how operating systems handle ARP updates.