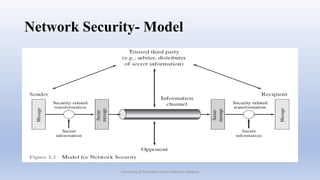
This document provides an introduction to a university course on network security. It outlines administrative details of the course such as the instructor, communication channels, class format, readings, and grading policy. It then defines key security concepts like confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It discusses security threats, attacks, and controls. It also provides examples of network security violations and outlines the OSI security architecture and a basic network security model. The goal is to give students an overview of fundamental network security principles.