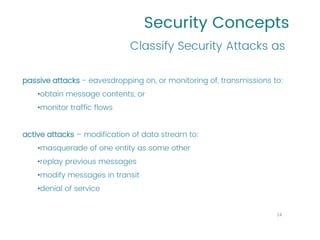
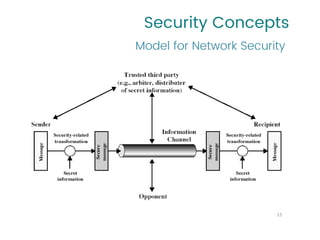
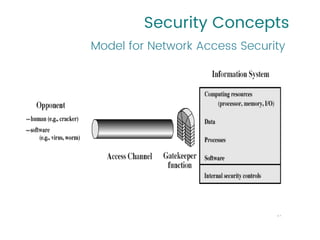
This document provides an overview of a university course on Cryptography and Network Security. It begins with the course syllabus, which outlines topics like security concepts, cryptography concepts and techniques, and types of security attacks. It then discusses key security concepts such as security services, security mechanisms, security attacks, and models for network and access security. It provides examples of security services like authentication, access control, and data confidentiality. It also describes security mechanisms and different classes of security attacks. The document concludes by listing reference books, online videos, related courses, tutorials, and sample multiple choice and problems related to cryptography and network security.