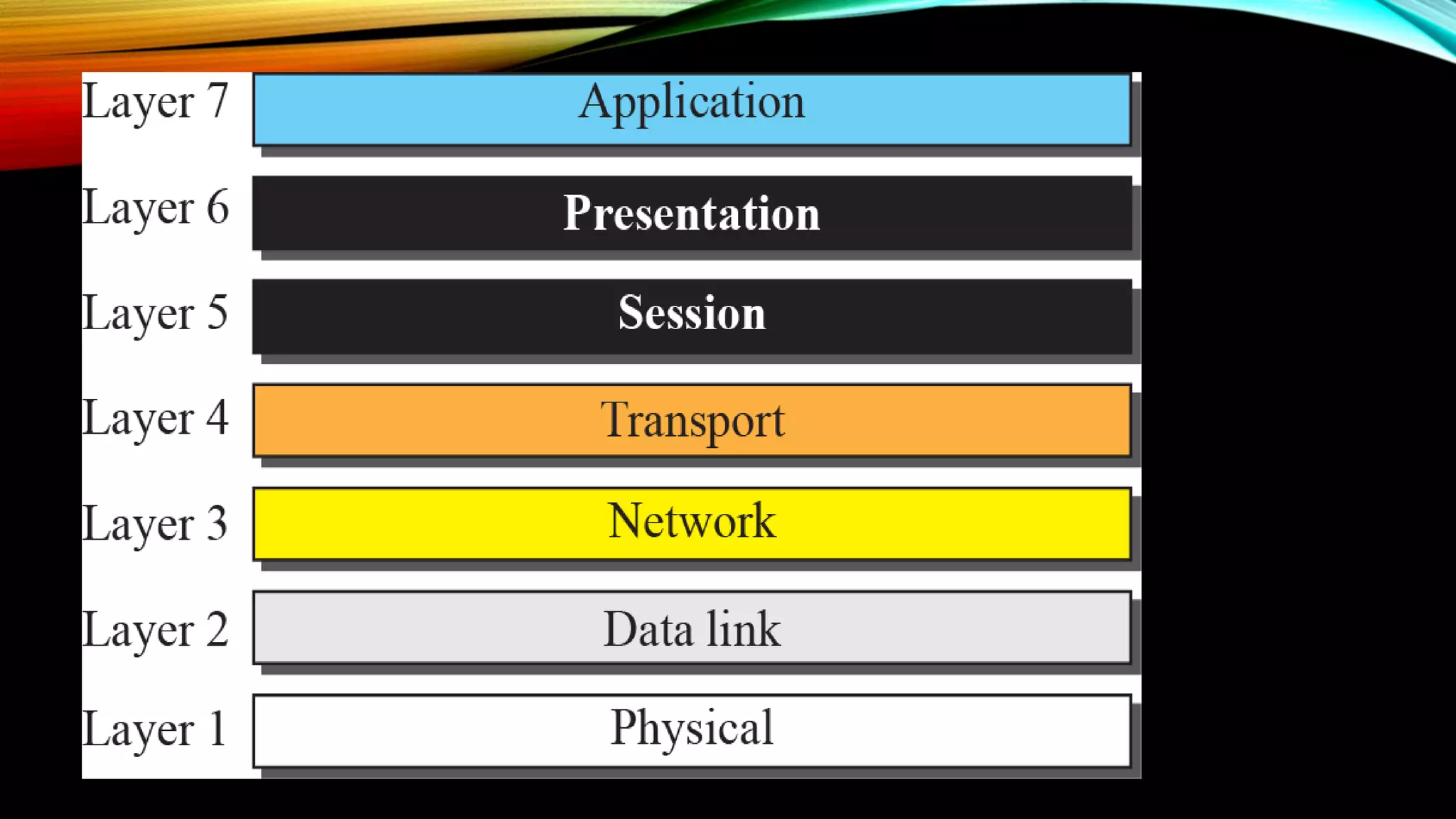
This document presents information on the OSI model for computer networking. It was presented by Anindya Nag and Rohit Sharma, third year B-Tech CSE students. There are two main models for data communication: the OSI model and the TCP/IP suite. The OSI model was developed by ISO and consists of 7 layers - physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application layer. The physical and data link layers are hardware layers, while the top three layers are software layers. The transport layer is called the heart of the OSI model. The OSI model follows a layered architecture to transmit data from sender to receiver through intermediate devices.


![Presented By:
•ANINDYA NAG &
• Rohit Sharma
•Roll No : UG/02/BTCSE/2018/005
•& Roll No: UG/02/BTCSE/2018/009
•B-Tech CSE , Section – “B” [3rd yr , 5th sem]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/random-210313054818/75/OSI-model-3-2048.jpg)