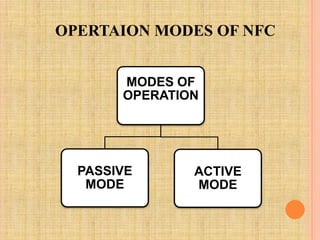
NFC allows short-range wireless communication between devices like phones and tags. It has two modes: passive, where one device provides power and the other receives it, and active, where both devices power their radios. NFC is used for applications like mobile payments and connecting devices for data transfer. It has a very short range under 50cm, low transfer rates, but high security and low cost. While useful for contactless transactions, its disadvantages are limited range and data speeds.