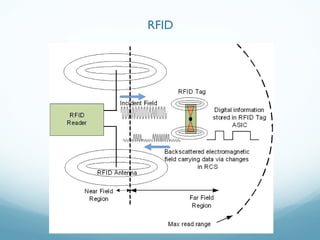
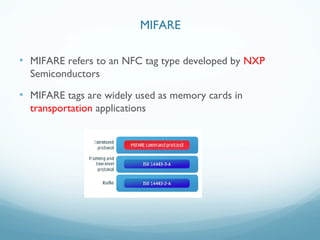
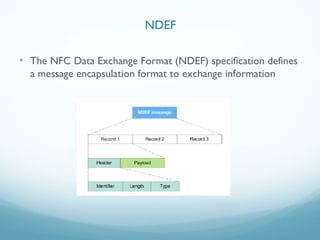
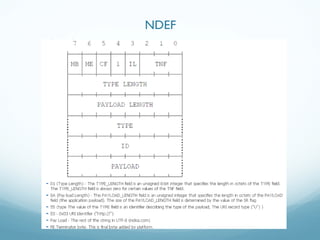
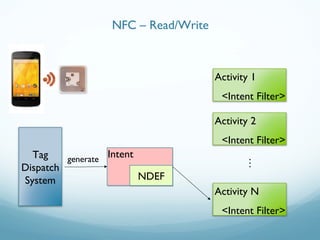
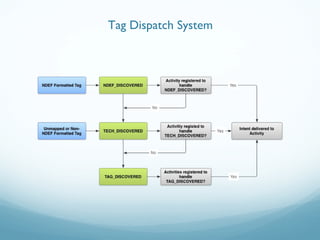
This document provides an introduction and overview of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. It discusses NFC use cases and the technical details of NFC, including the different tag types, specifications, and communication modes. It then focuses on how NFC is implemented on Android devices, explaining how the tag dispatch system works to retrieve data from NFC tags and route intents to the appropriate applications based on the data and intent filters. Examples are provided of creating NDEF messages and corresponding intent filters for different data types.