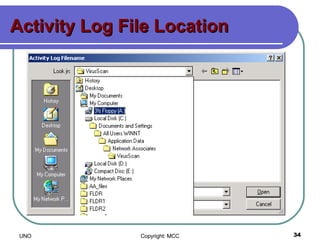
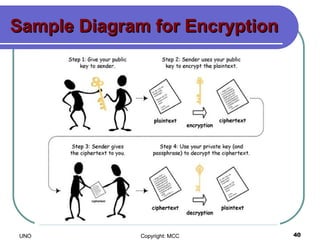
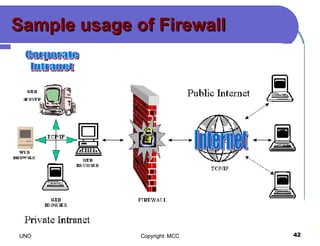
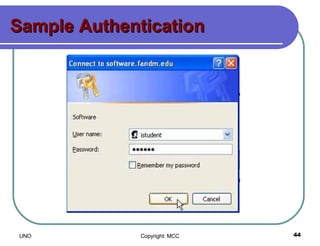
This document provides an overview of computer viruses and data security topics. It discusses different types of malware like viruses, worms, Trojan horses and hybrids. It also covers topics like encryption, firewalls, authentication, virtual private networks, digital certificates, digital signatures, certification authorities and online security assistants. The document aims to educate about computer viruses, data security issues and how to prevent and protect against malware.











![What is SPAM? "Spamming [the sending of unsolicited email] is the scourge of electronic-mail and newsgroups on the Internet. It can seriously interfere with the operation of public services, to say nothing of the effect it may have on any individual's e-mail mail system. Spammers are, in effect, taking resources away from users and service suppliers without compensation and without authorization."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ne-course-part-one-1196006876115328-4/85/Ne-Course-Part-One-14-320.jpg)