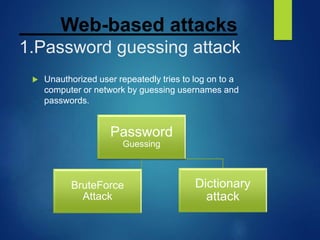
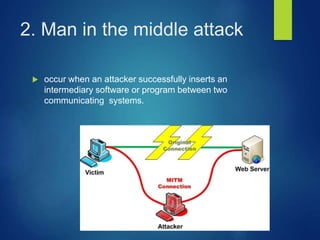
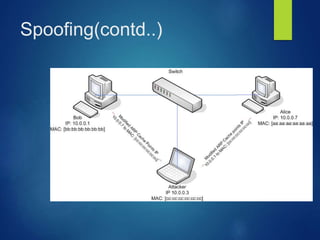
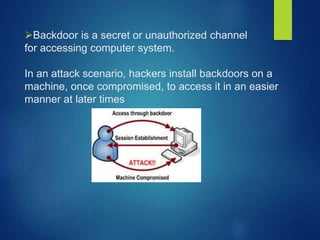
This document discusses types of cyber attacks, including web-based attacks like password guessing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and phishing. It also discusses system-based attacks such as spoofing, backdoors, viruses, worms, and Trojan horses. Password guessing attacks can include brute force or dictionary attacks. Man-in-the-middle attacks intercept communications. Phishing involves deception to steal personal information. Spoofing modifies packet headers to hide identity. Backdoors bypass security checks. Viruses and worms can self-replicate and spread. Trojan horses claim to do one thing but actually cause harm.