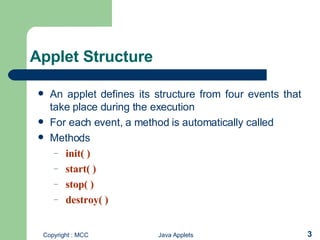
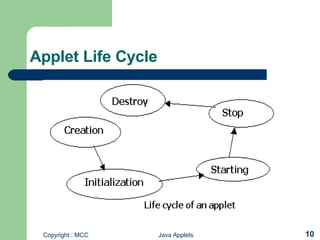
- Java applets allow Java programs to run within web browsers. All applets extend the Applet class and override lifecycle methods like init(), start(), stop(), and destroy().
- To create an applet, you define its structure using these lifecycle methods and draw to the screen using the Graphics object's drawing methods. Applets are compiled and run within HTML using the <applet> tag.
- Applets differ from standalone Java applications in that they have security restrictions and run within a web browser rather than having their own execution environment. The Graphics class provides methods for drawing various shapes, text, and images to the applet display area.




![Example of Applet (Cont] <html> <head> <title>Hello World</title> </head> <body> This is an applet<p> <applet codebase=“classes” code=“HelloWorldApplet.class” width=200 height=300></applet> </body> </html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/client-side-programming-with-applet-1197644957354286-5/85/Client-Side-Programming-with-Applet-7-320.jpg)




![Drawing Strings, Characters and Bytes Method to draw or print a string on the frame Syntax drawString(String str, int xCoor, int yCoor); Method to draw or print characters on the frame Syntax drawChars(char array[ ], int offset, int length, int xCoor, int yCoor); Method to draw or print bytes on the frame Syntax drawBytes(byte array[ ], int offset, int length, int xCoor, int yCoor);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/client-side-programming-with-applet-1197644957354286-5/85/Client-Side-Programming-with-Applet-14-320.jpg)



![Drawing PolyLines Methods used to draw a series of lines Syntax drawPolyline(int xArray[ ], int yArray[ ], int totalPoints); g.setFont(new Font("Times Roman", Font.BOLD,15));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/client-side-programming-with-applet-1197644957354286-5/85/Client-Side-Programming-with-Applet-18-320.jpg)
![Drawing and Filling Polygons Methods to draw and fill polygons Syntax drawPolygon(int x[ ], int y[ ], int numPoints); fillPolygon(int x[ ], int y[ ], int numPoints);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/client-side-programming-with-applet-1197644957354286-5/85/Client-Side-Programming-with-Applet-19-320.jpg)





![Exercise 2 import java.applet.Applet; import java.awt.*; /* <applet code = “both” width = 200 height = 100 > </applet> */ public class both extends Applet { Button btn; public void init() { btn = new Button(“Click”); } public void paint(Graphics g) { g.drawString(“Applet”, 70, 50 ); } public static void main(String args[]) { both app=new both(); app.init(); System.out.println(“Application Main”); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/client-side-programming-with-applet-1197644957354286-5/85/Client-Side-Programming-with-Applet-27-320.jpg)