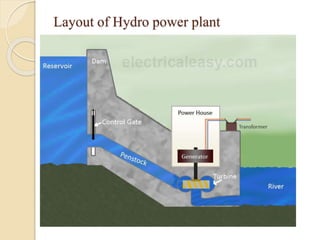
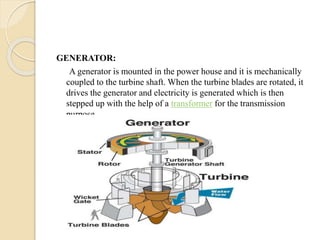
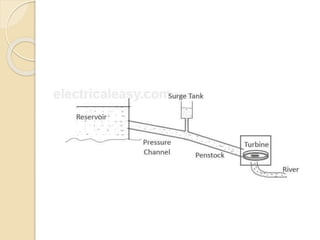
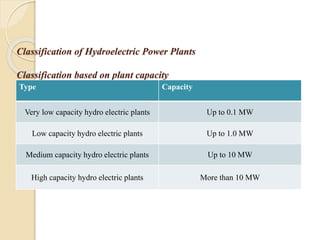
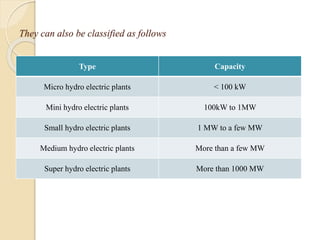
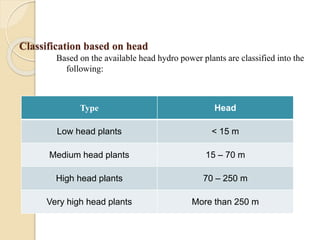
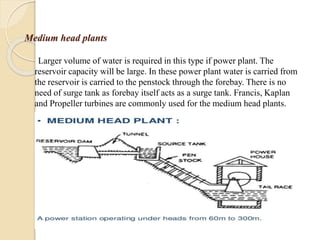
This technical seminar report details the construction and operation of hydroelectric power plants, focusing on how electricity is generated using water as a resource. It covers the layout, components like dams, penstocks, and turbines, and classifies hydro power plants based on capacity and head. The report concludes with the advantages and disadvantages of hydroelectric power, noting its historical significance and current market stagnation.