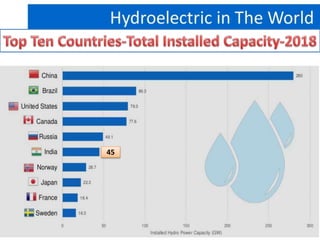
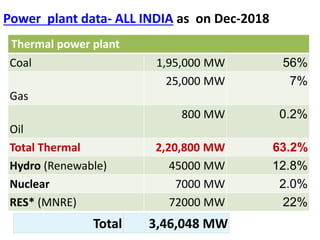
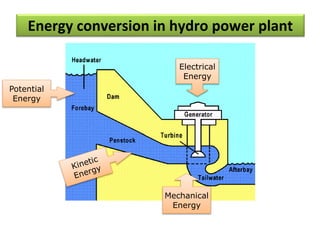
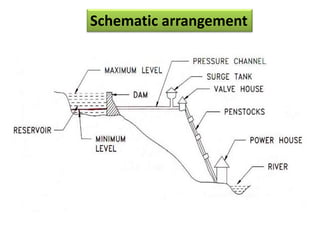
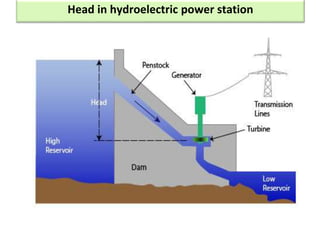
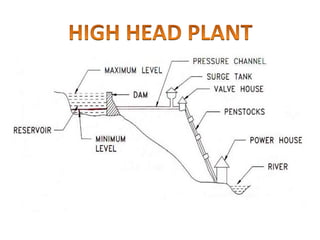
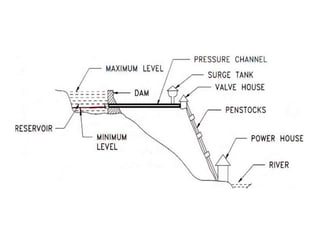
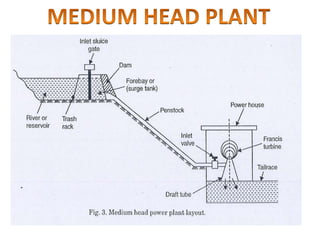
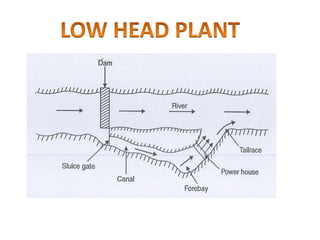
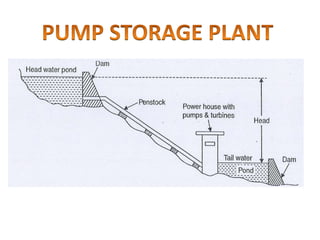
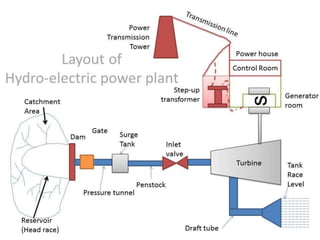
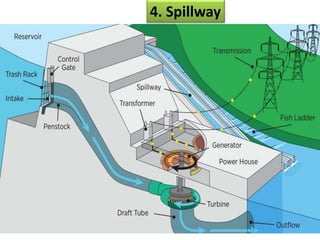
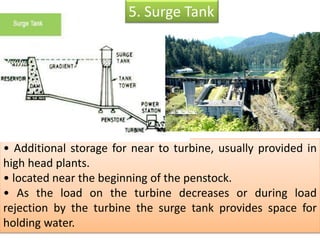
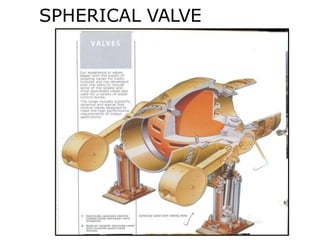
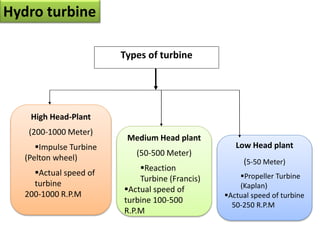
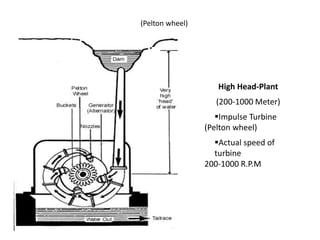
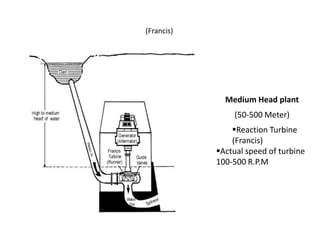
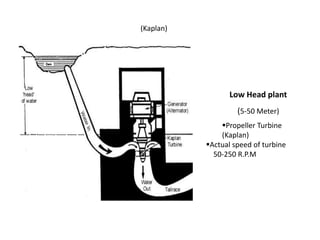
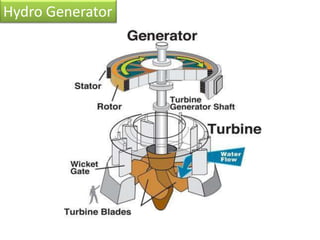
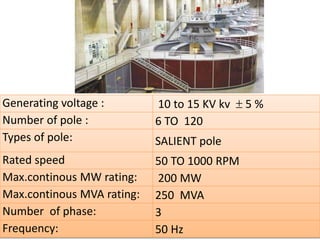
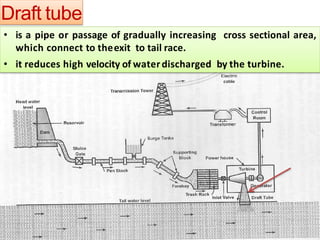
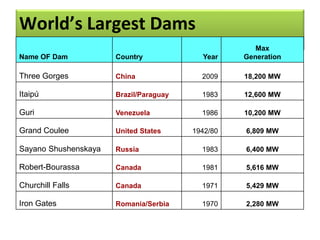
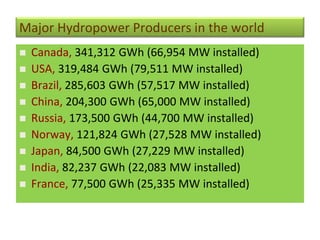
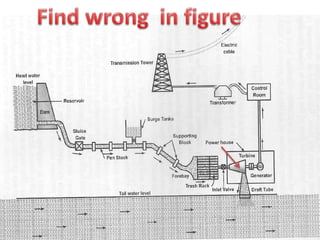
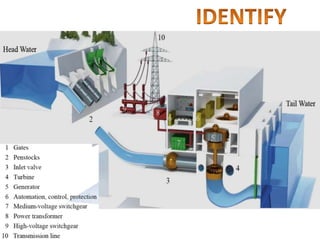
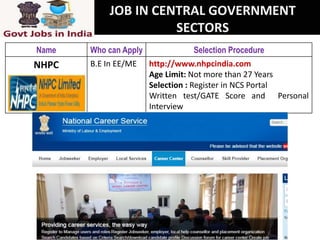
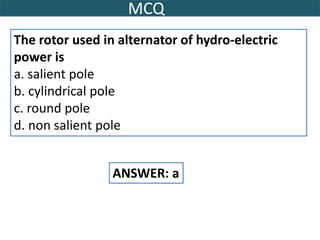
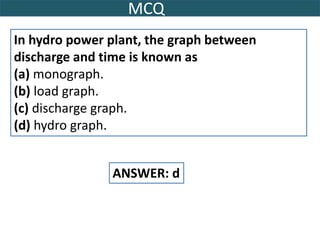
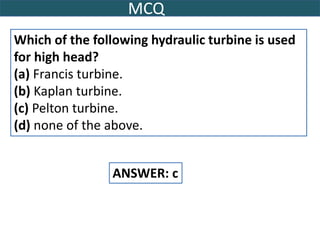
This document provides information on hydro power stations, including their schematic arrangement, classification, advantages and disadvantages, site selection criteria, and environmental impacts. It discusses the key components of a hydro power plant such as the catchment area, dam, reservoir, penstocks, valves, turbines, generators, and draft tubes. It also lists the largest hydro power producers in the world and provides examples of major hydro power projects in India along with career opportunities in the hydro power sector.