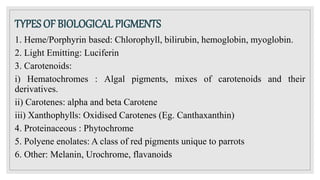
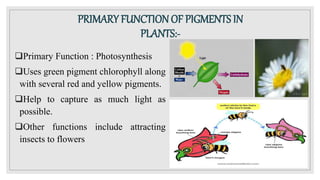
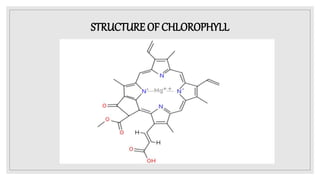
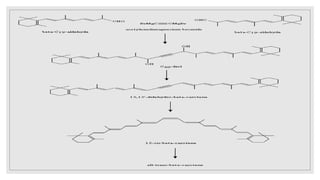
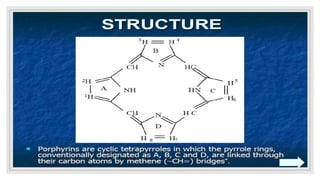
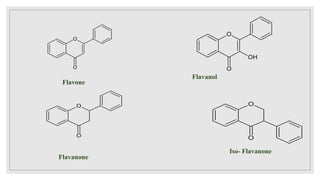
The document discusses natural pigments, defining them as molecules that absorb specific wavelengths of light and outlining their classification, structure, and synthesis. It distinguishes between pigment color and structural color, explaining various types of biological pigments and their roles, particularly in plants for photosynthesis. The primary pigments mentioned include chlorophyll, carotenoids, xanthophylls, and anthocyanins, highlighting their importance in capturing light and attracting pollinators.