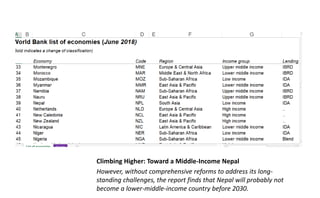
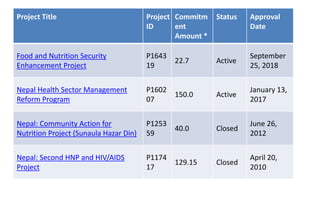
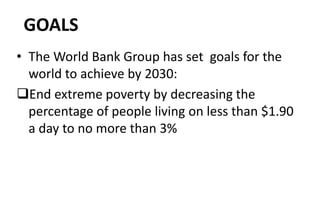The document provides information about the World Bank, including that it is an international organization that provides financial and technical assistance to developing countries with the goal of reducing poverty. It loans money to these countries for projects focused on areas like education, health, infrastructure, and more. The World Bank consists of five institutions and has over 180 member countries. It works on issues such as agriculture, climate, education, health, and aims to end extreme poverty by 2030. In Nepal, the World Bank has funded several health projects focused on nutrition, health systems, and more.