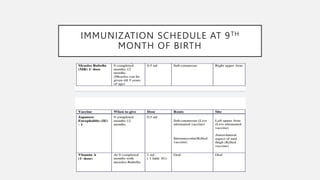
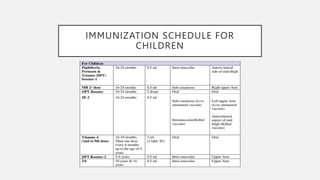
The document discusses the significance of vaccination as a cost-effective public health strategy and highlights the Universal Immunization Program (UIP) launched by the Indian government in 1985. The UIP has expanded to include vaccines for 12 diseases and introduced various vaccines over the years, emphasizing the program's role in reducing disease spread and improving health outcomes. It also outlines the national immunization schedule for infants, children, and pregnant women.


![UNIVERSAL IMMUNIZATION PROGRAM
• Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP) is a vaccination programme
launched by the Government of India in 1985.
• It became a part of Child Survival and Safe Motherhood Programme in
1992 and is currently one of the key areas under National Rural Health
Mission since 2005. The programme now consists of vaccination for 12
diseases- tuberculosis, diphtheria, pertussis (whooping cough), tetanus,
poliomyelitis, measles, hepatitis B, diarrhoea, Japanese encephalitis,
rubella, pneumonia (haemophilus influenza type B) and Pneumococcal
diseases (pneumococcal pneumonia and meningitis). Hepatitis B and
Pneumococcal diseases[2] were added to the UIP in 2007 and 2017
respectively.
• The other additions in UIP through the way are inactivated polio vaccine
(IPV), rotavirus vaccine (RVV), Measles-Rubella vaccine (MR). Four new
vaccines have been introduced into the country’s Universal
Immunisation Programme (UIP), including injectable polio vaccine, an
adult vaccine against Japanese Encephalitis and Pneumococcal
Conjugate Vaccine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nationalimmunisationprogram-240224111918-c7cb0bb1/85/National-Immunisation-Program-India-2022-3-320.jpg)