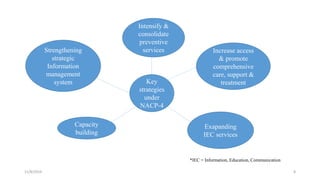
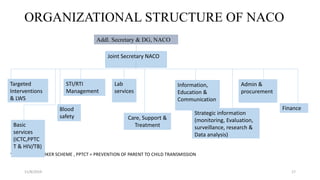
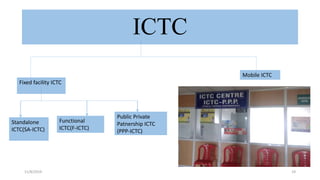
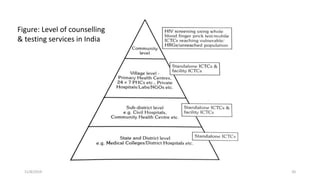
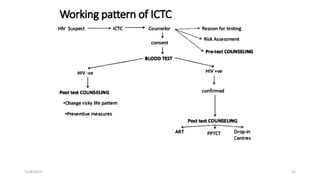
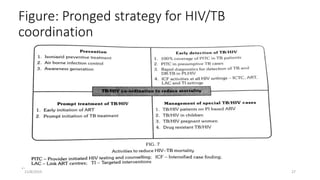
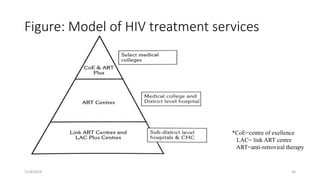
The National AIDS Control Programme was launched in India in 1987 with the aims of preventing HIV transmission, decreasing morbidity and mortality associated with HIV infection, and minimizing the socioeconomic impact of HIV infection. Key milestones and strategies of the program include establishing surveillance centers, identifying and screening high-risk groups, and expanding access to counseling, testing, treatment and support services. The government has implemented multiple phases of the program to scale up prevention, care and treatment efforts across the country.