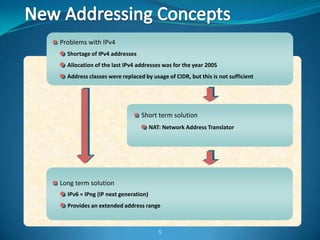
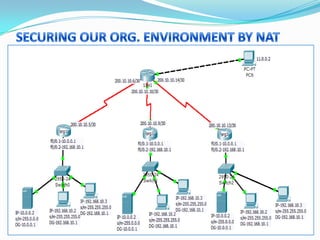
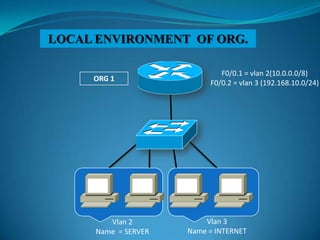
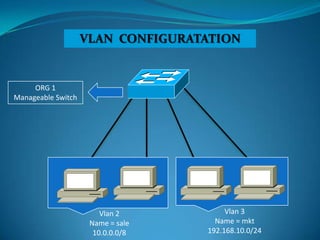
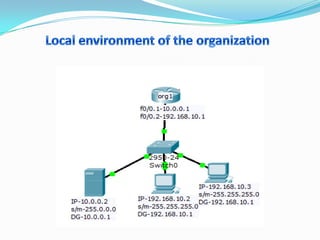
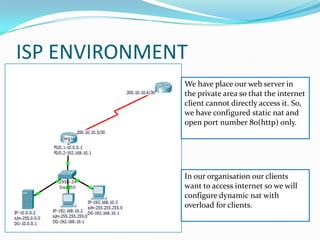
1. Configure VLANs to separate servers and clients in each organization.
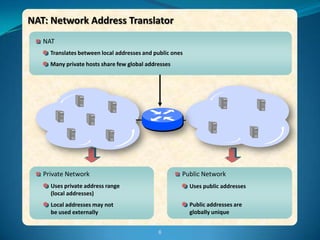
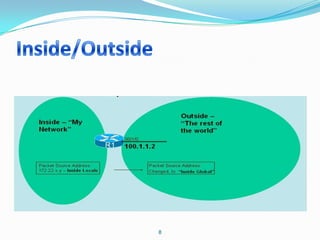
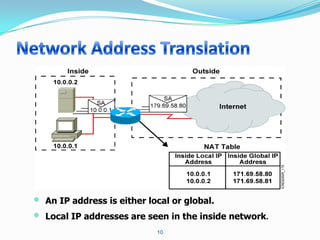
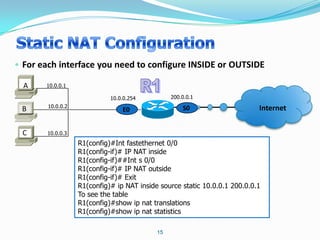
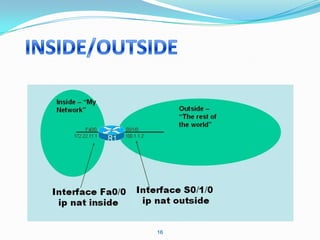
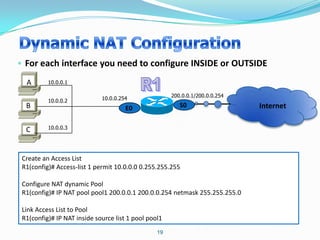
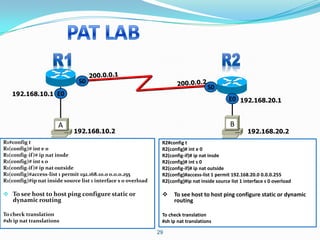
2. Configure NAT inside and outside interfaces on routers.
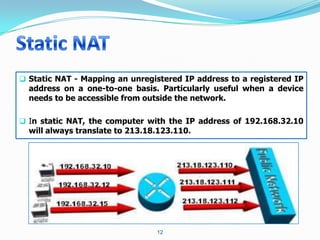
3. Use static NAT to expose a server to the internet with port forwarding.
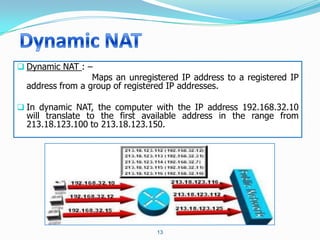
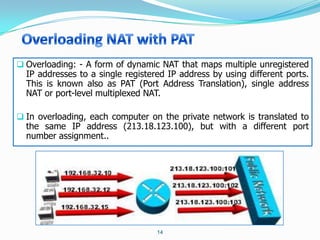
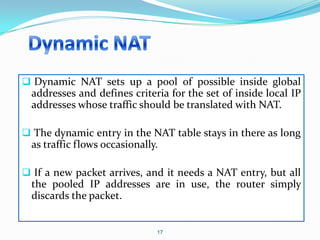
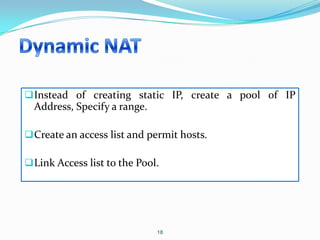
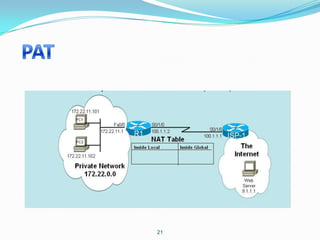
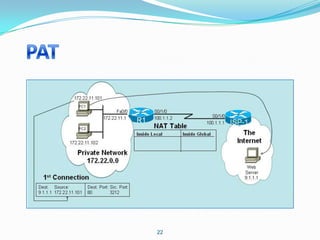
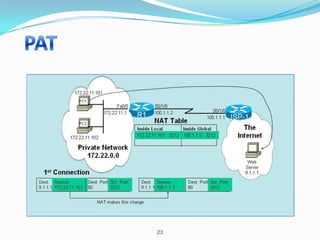
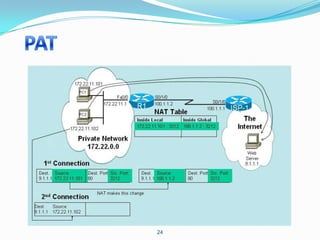
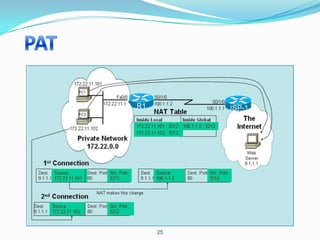
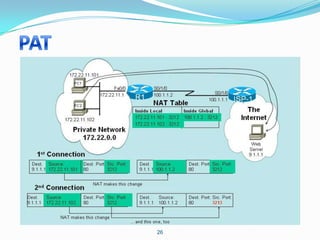
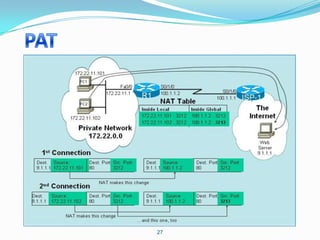
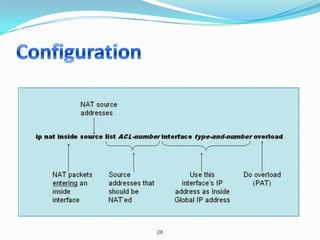
4. Use dynamic NAT with overload for internet access for internal clients, sharing a public IP.
This allows internal clients to access external servers while protecting internal servers from direct internet access. The ISP provides public IPs for NAT translations between the private and public networks.