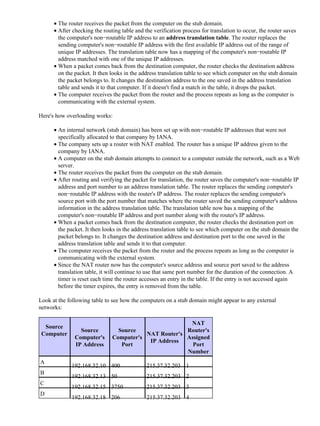
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows a single device such as a router to act as an agent between an internal private network and the public internet. NAT conserves IP addresses by mapping multiple unregistered private IP addresses to a single registered public IP address. There are different types of NAT including static NAT which maps private to public addresses on a one-to-one basis, dynamic NAT which maps to available public addresses, and port address translation (PAT) which overloads a public IP address by using different port numbers for each private address. NAT translates IP addresses for traffic entering and leaving the private network to allow communication while hiding the internal network topology.