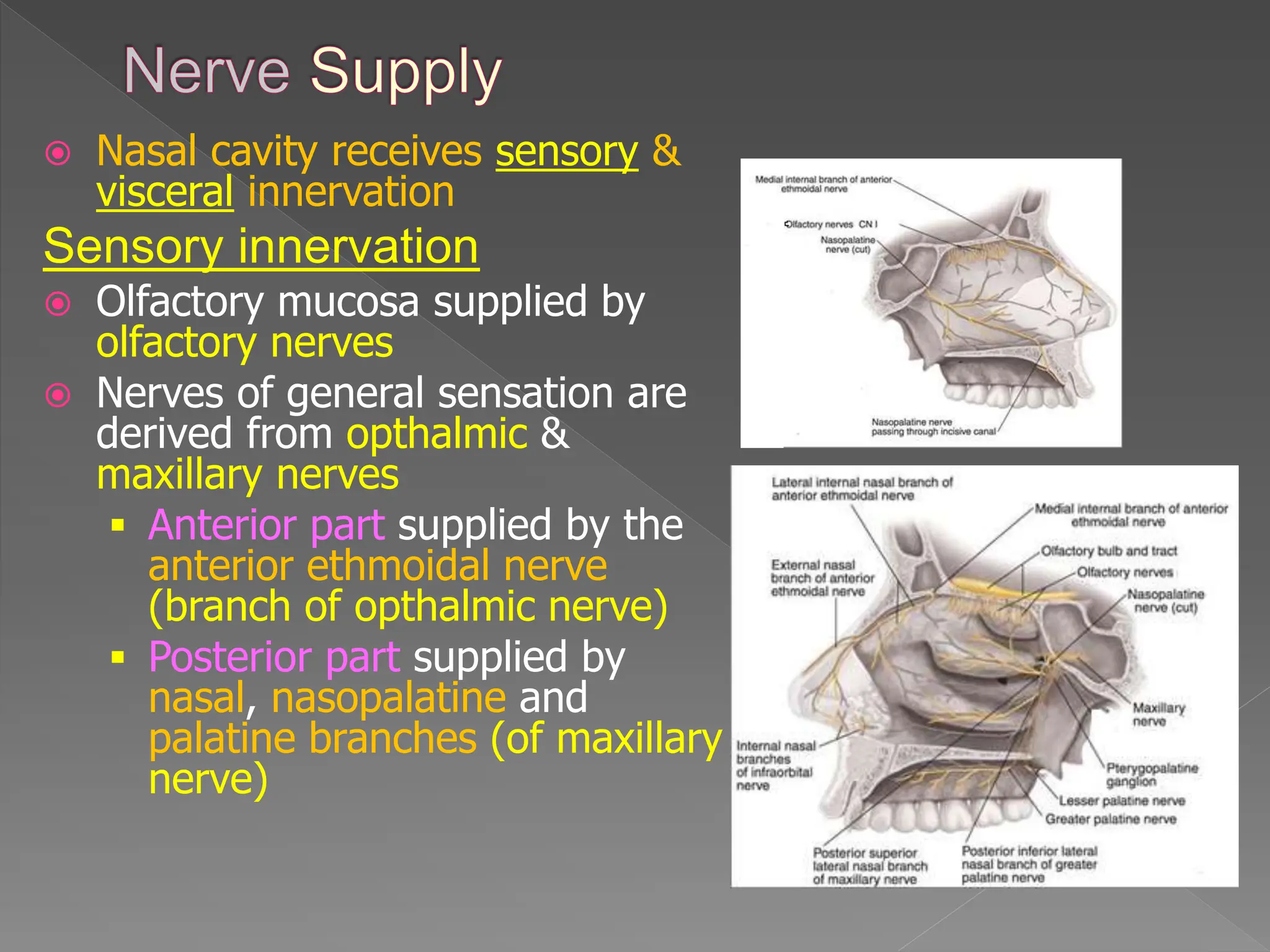
The nose is an externally visible structure with two nostrils that lead to the nasal cavity. The nasal cavity is divided by the nasal septum and contains conchae which increase its surface area. It is lined by olfactory and respiratory mucosa and contains olfactory receptors. The nasal cavity conditions inhaled air and drains into the throat. It is associated with paranasal sinuses which lighten the skull and modify voice. Common nasal disorders include epistaxis and sinusitis.