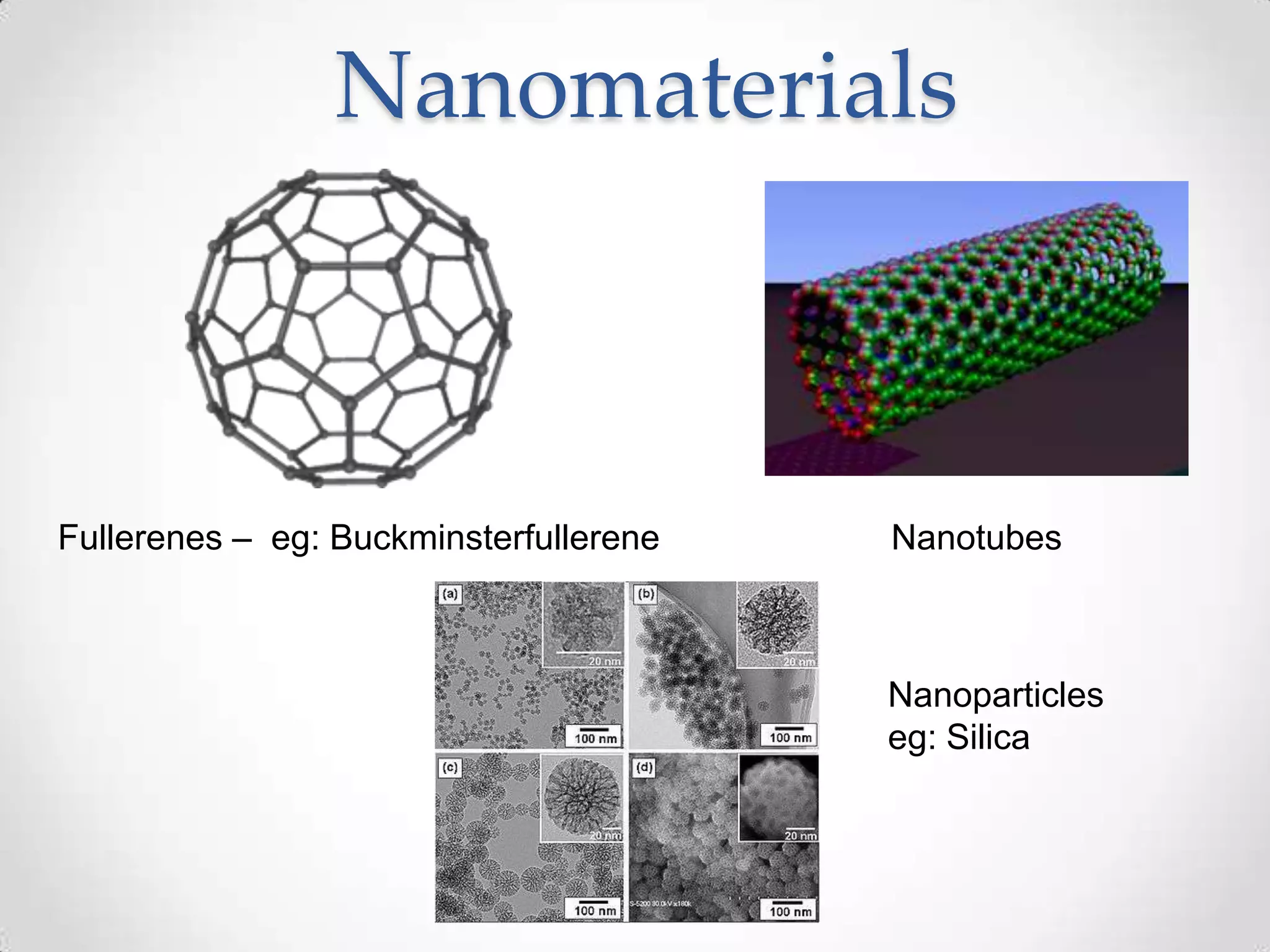
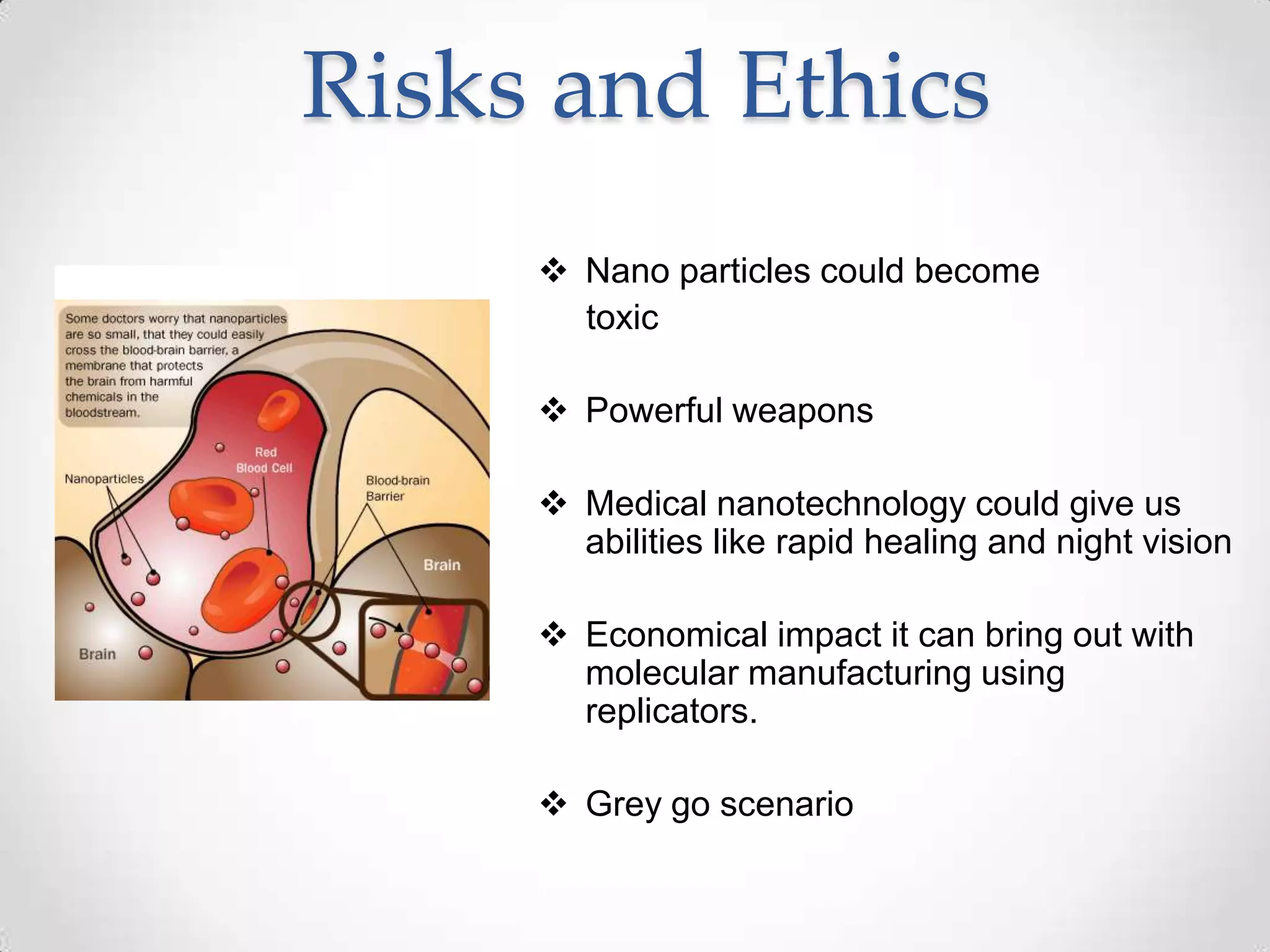
The document discusses nanotechnology, including its definition as the study of phenomena on the nanoscale, less than 100 nanometers. It describes nanomaterials like fullerenes and nanoparticles. Applications of nanotechnology mentioned include sunscreen, scratch-resistant coatings, microprocessors, and medicine. The future of nanotechnology may include replicating machines, addressing issues like the ozone layer with airborne nanobots, and targeting cancer cells with nano-robots. Risks discussed include toxicity of nanoparticles and potential weapons applications.