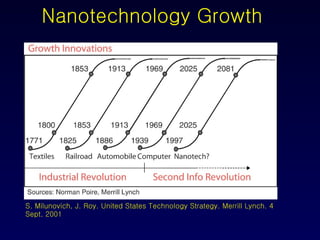
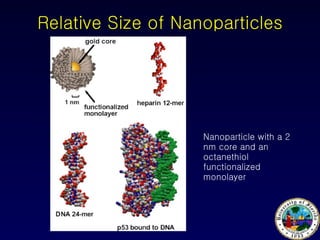
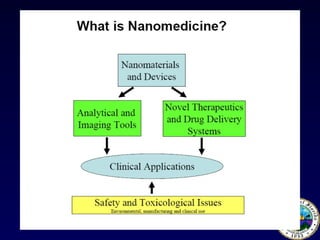
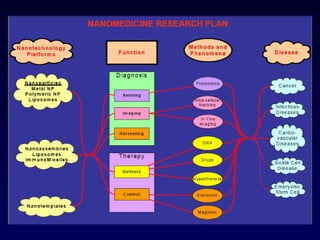
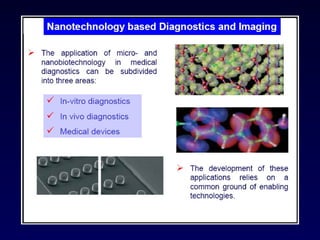
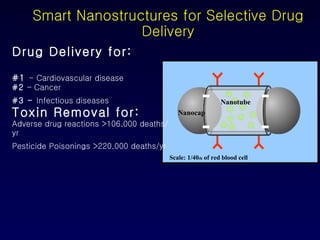
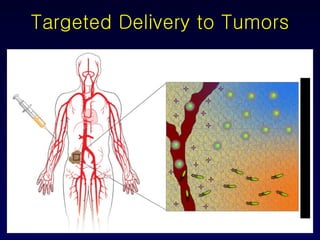
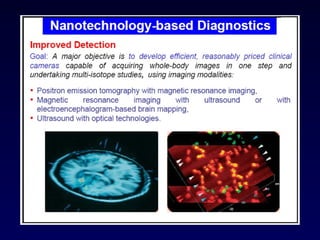
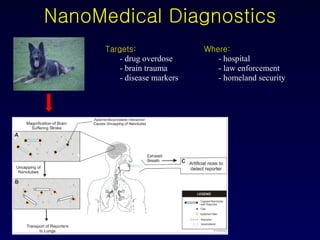
Nanotechnology involves controlling and manipulating matter on the nanometer scale (1-100 nm) to develop novel materials and devices. It has grown significantly with many medical applications such as targeted drug delivery using smart nanostructures to treat diseases like cancer and cardiovascular issues. Nanomedicine also enables diagnostic tools to detect conditions and toxins in the body through methods that could be used in hospitals, law enforcement, and homeland security.