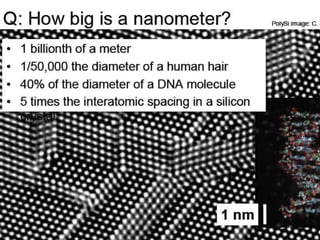
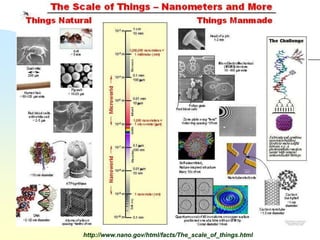
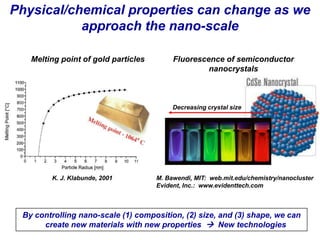
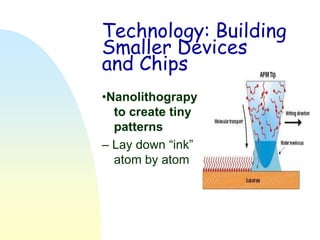
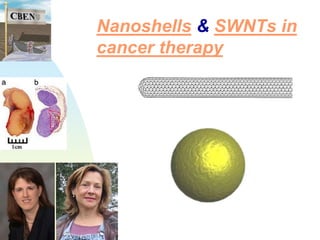
Nanotechnology involves studying and manipulating matter at the nanoscale, between 1-100 nanometers. At this scale, materials exhibit different physical and chemical properties than at larger scales due to factors like high density and changes in how properties scale with dimension. Researchers are working to develop new materials and technologies by controlling composition, size, and shape at the nanoscale. Some potential applications of nanotechnology include stain-resistant clothing, self-cleaning paint, more efficient solar cells, smaller computing devices, earlier disease detection, and nerve tissue interfacing with computers. Cancer therapies also utilize nanoparticles for localized heating or drug delivery to tumors.