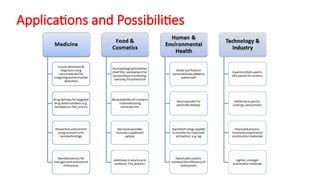
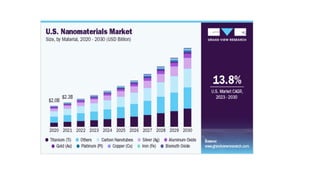
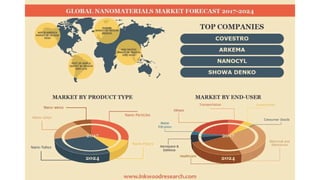
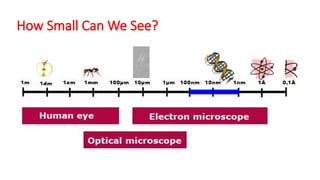
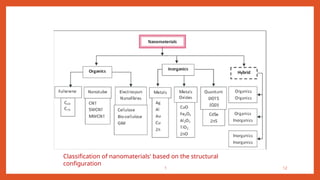
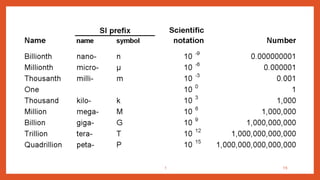
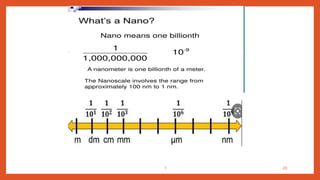
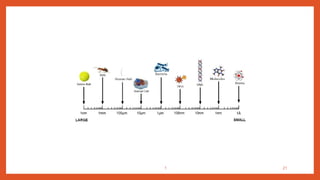
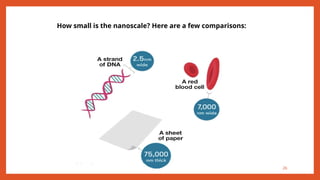
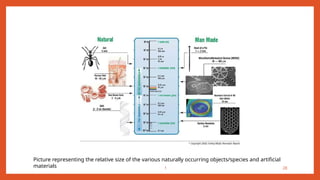
Nanotechnology is the scientific study and manipulation of materials at the nanoscale, specifically between 1 to 100 nanometers. It enables the creation of new materials and devices with unique properties, playing a critical role in medicine, electronics, and energy. Nanomaterials, defined by their structural components at nanoscale, exhibit enhanced physical and chemical properties, leading to a wide range of applications.