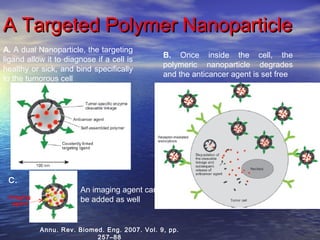
Nanoparticles show promise for improving cancer diagnosis and treatment. They can be used to detect cancer by carrying imaging agents targeted to tumor biomarkers (A). For treatment, nanoparticles can deliver higher doses of chemotherapy drugs specifically to cancer cells, reducing toxicity to healthy cells (B). Biodegradable polymer nanoparticles have been designed to both target tumor cells using ligands, diagnose the cells, and release anticancer drugs inside the cells to treat the cancer (C). Overall, nanoparticles may enable more effective and less toxic cancer diagnosis and therapy by taking advantage of their small size and ability to be functionalized for targeting.