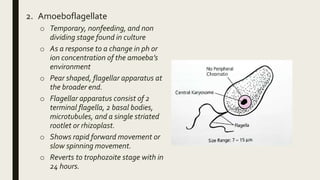
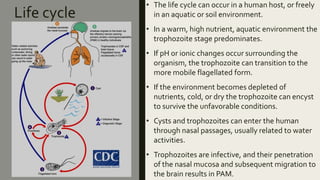
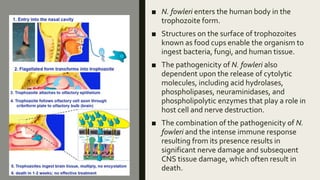
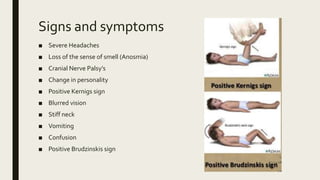
Naegleria fowleri, commonly known as the "brain-eating amoeba", is a free-living microscopic amoeba found in warm freshwater and soil. It usually infects humans when contaminated water enters the body through the nose. It then travels to the brain where it causes primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), which is usually fatal. PAM symptoms include severe headaches, fever, stiff neck, seizures and coma. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of CSF or brain tissue for the presence of trophozoites. Treatment involves the antifungal drug amphotericin B, though PAM often proves fatal.