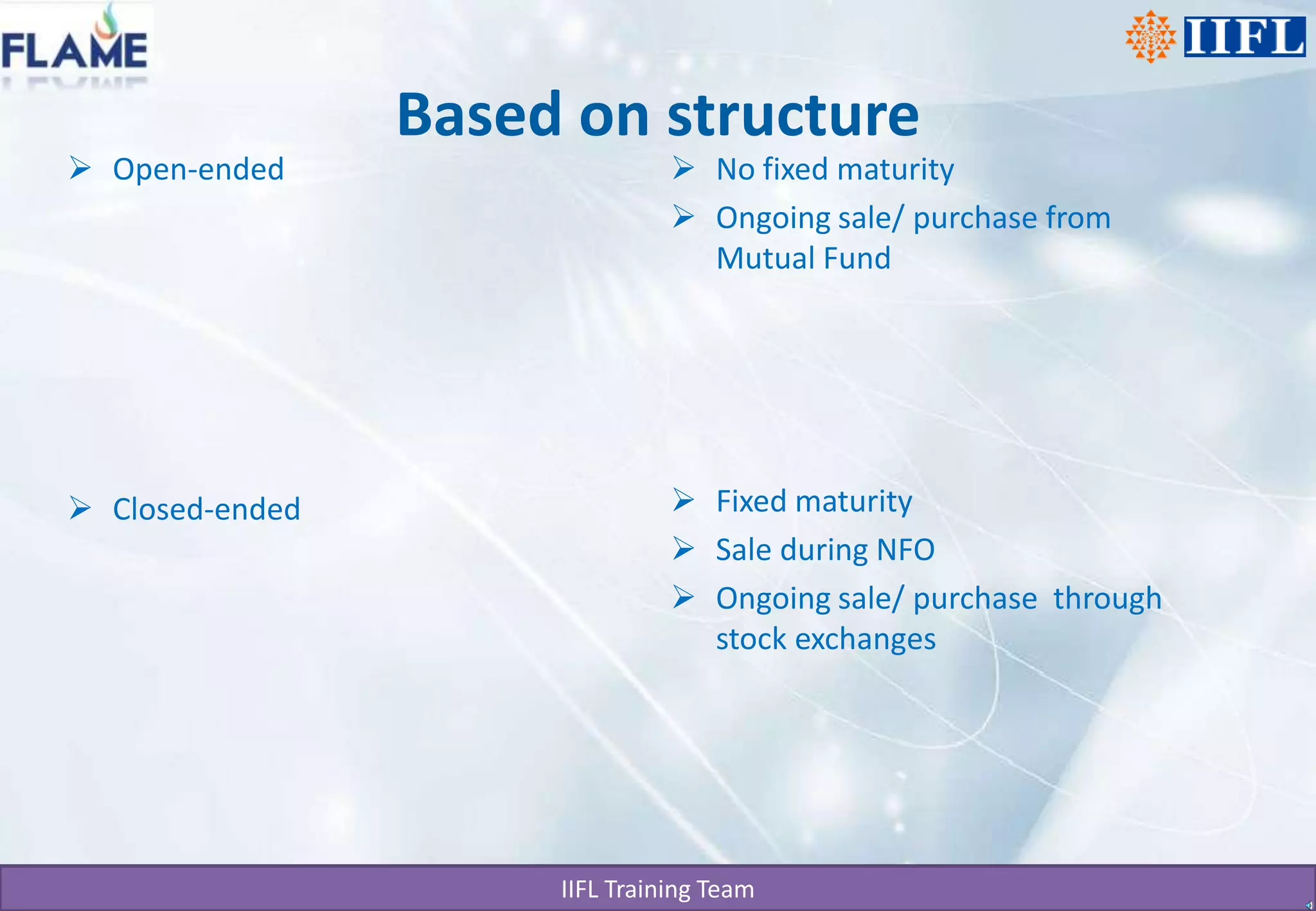
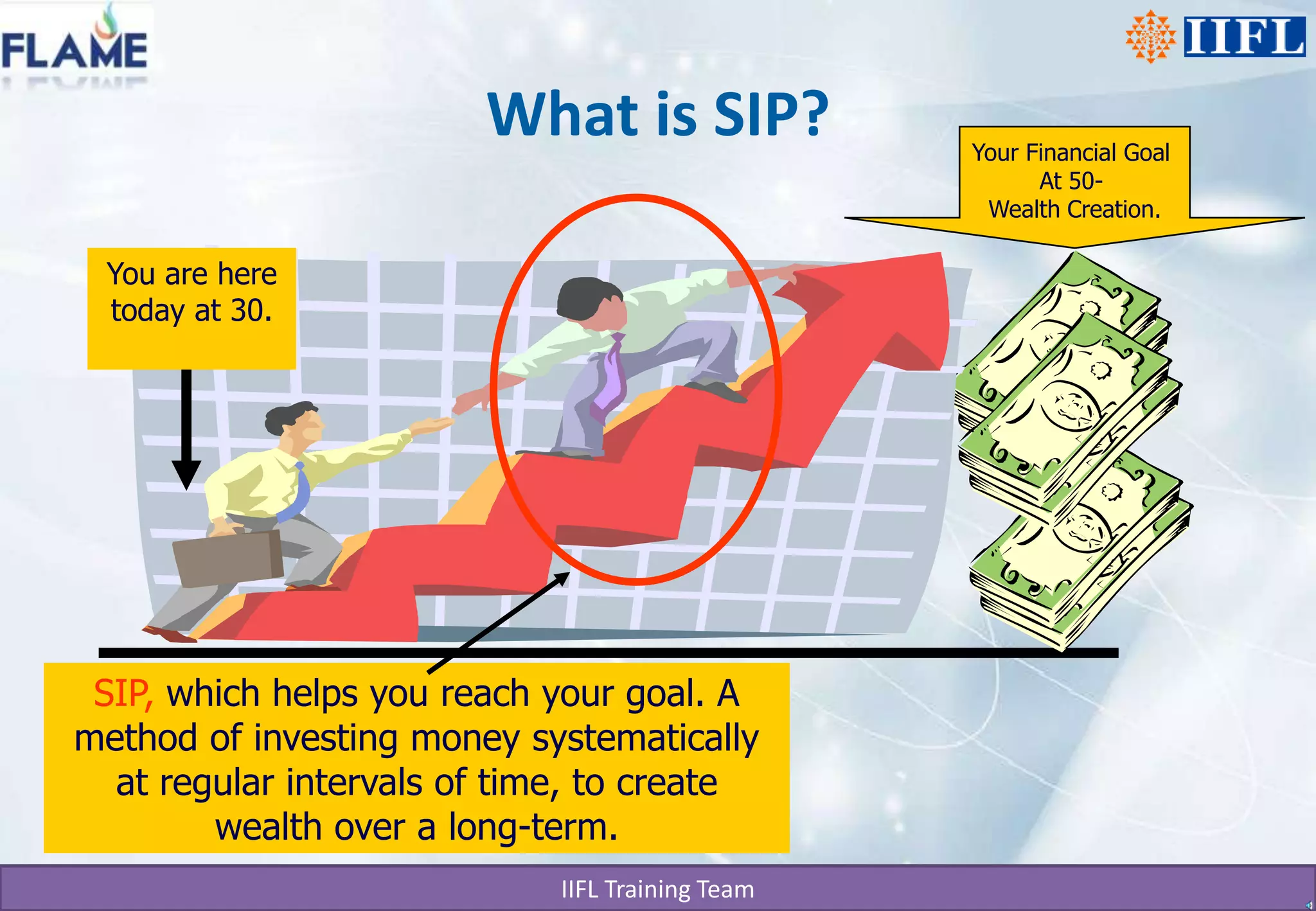
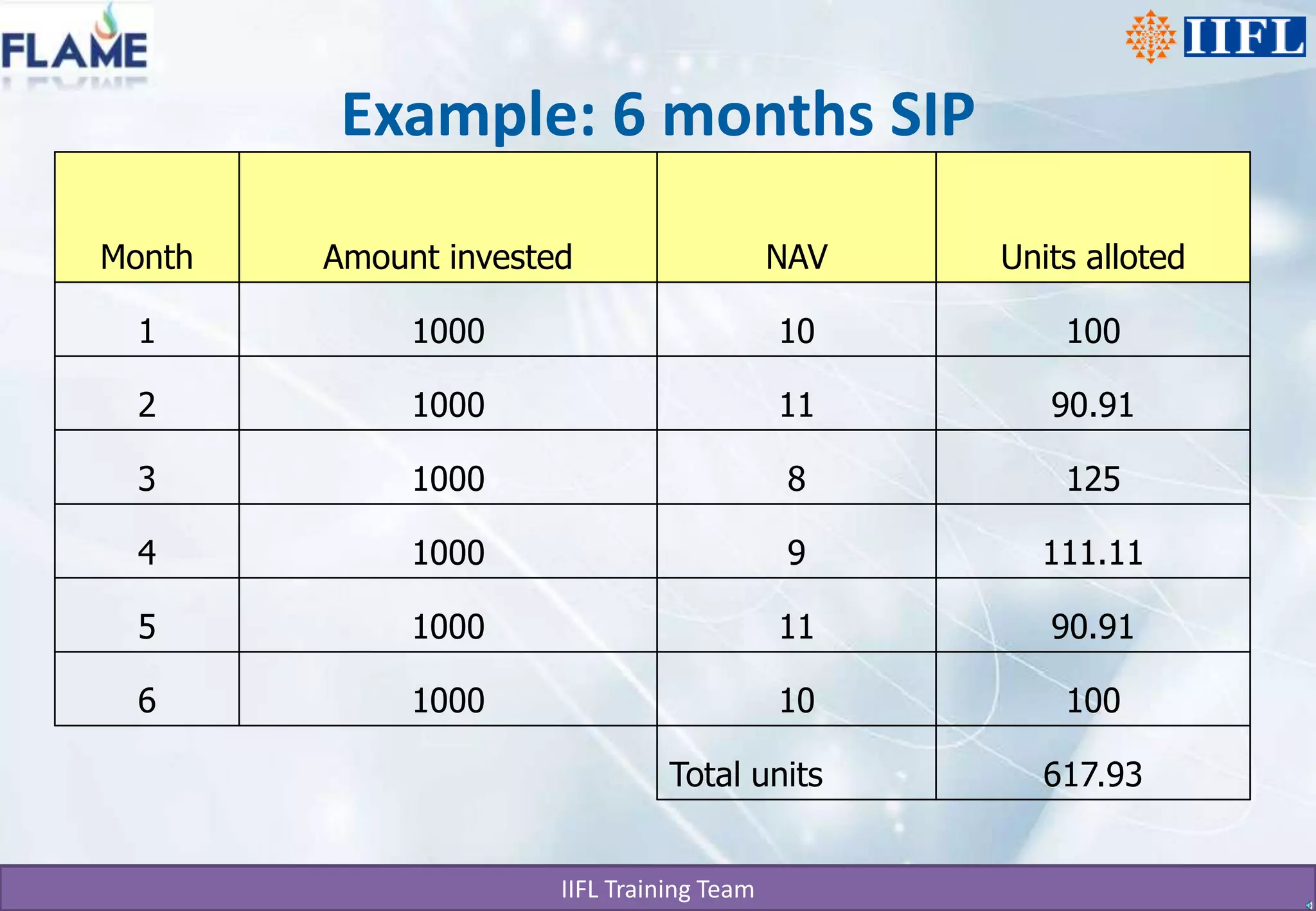
The document discusses different types of mutual funds categorized by structure, market capitalization, and investment objective. It describes open-ended and closed-ended funds, as well as large cap, mid cap, and small cap funds. Funds are also classified based on whether they focus on growth, hybrid, or debt investments. The key benefits of mutual funds include professional management, diversification, convenience, return potential, low costs, liquidity, transparency, flexibility, affordability, and a wide choice of schemes. SIP and STP are also summarized as systematic investment and transfer plans that allow regular investing in mutual funds to build wealth over the long term.