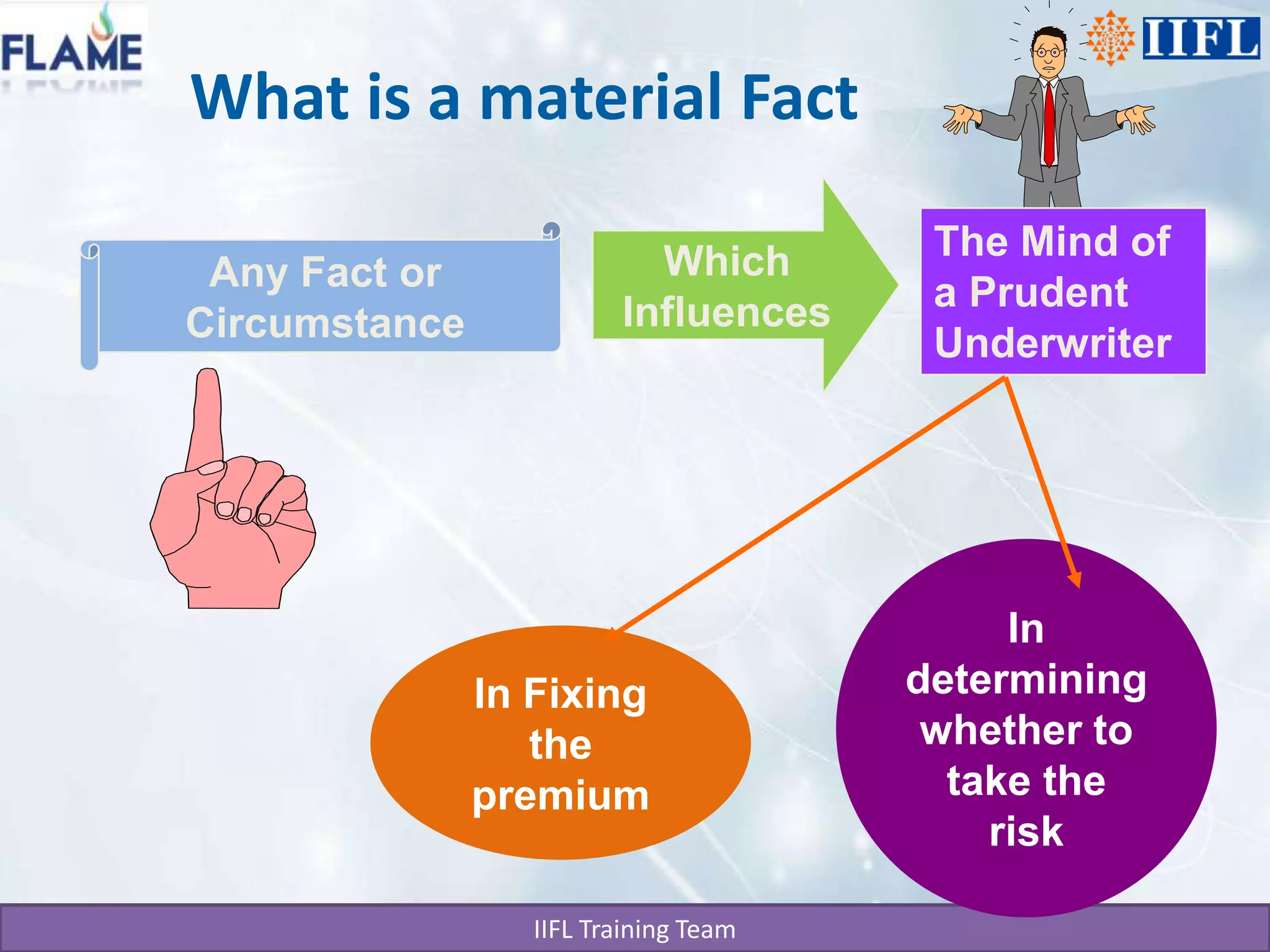
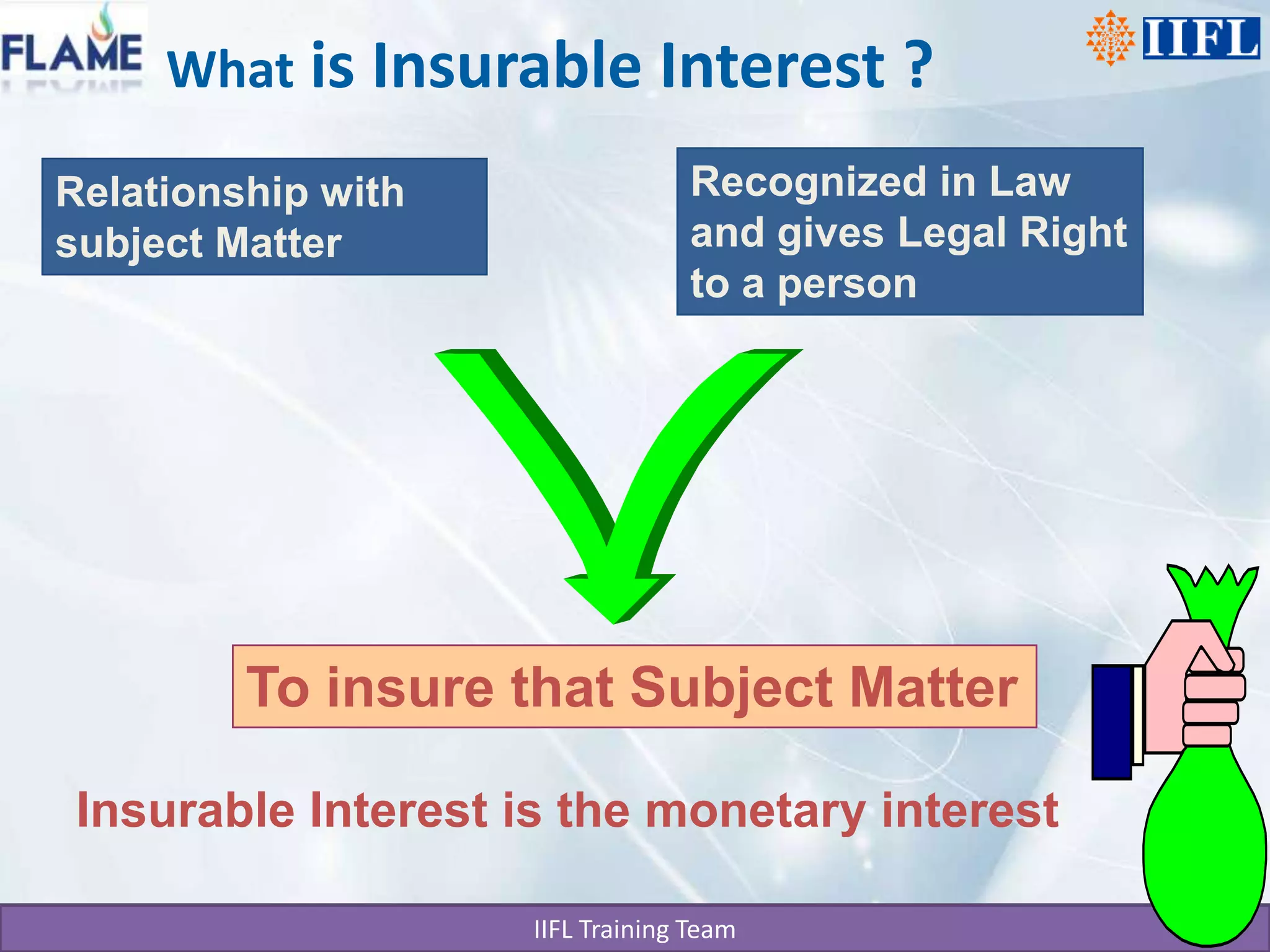
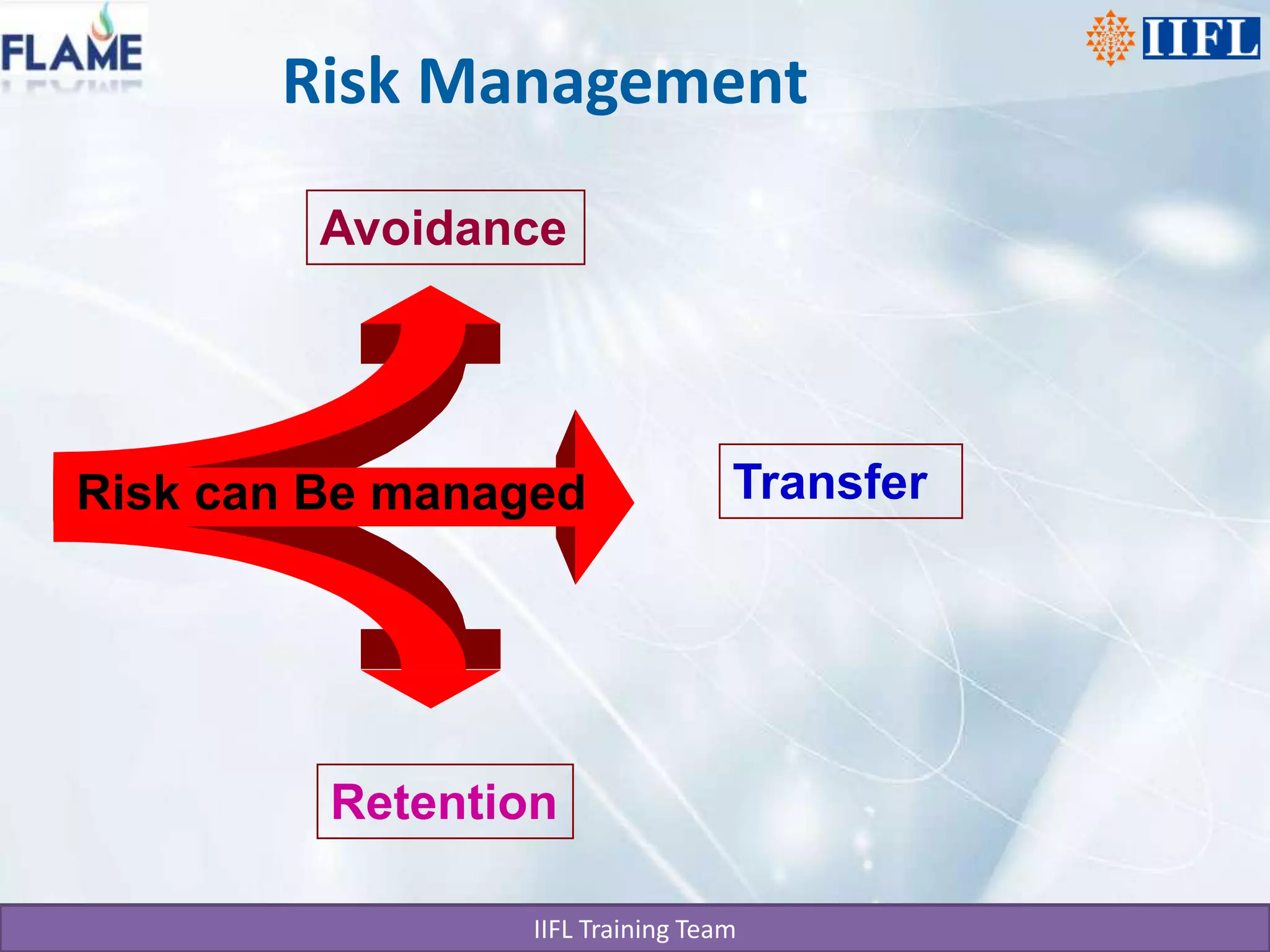
This document discusses the basics of life insurance principles in India. It explains that a life insurance policy is a legal contract that requires utmost good faith between the insurer and insured. The insured must disclose all material facts fully and accurately. If any material facts are found to be misrepresented or not disclosed within two years, the insurer can declare the policy null and void. To take a policy, the insured must have an insurable interest, which is a monetary interest, in the subject being insured. The principles of indemnity and risk management also apply to insurance contracts.