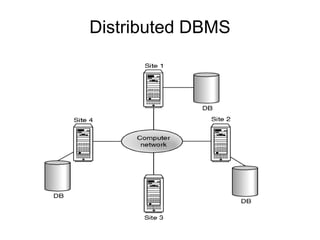
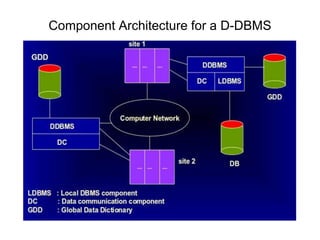
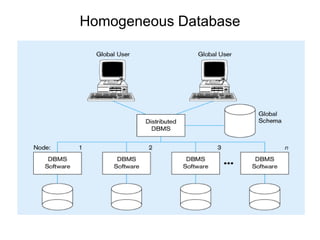
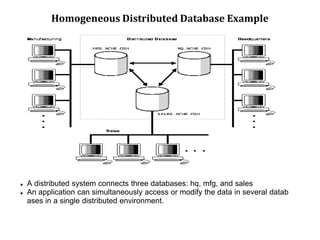
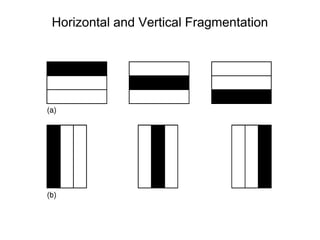
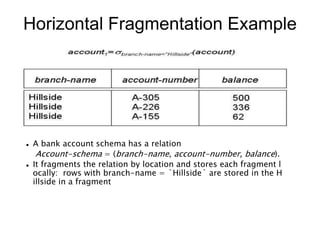
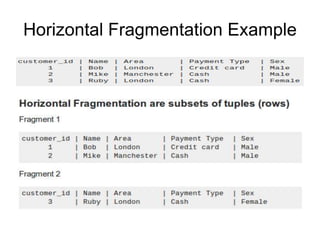
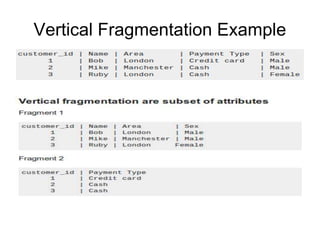
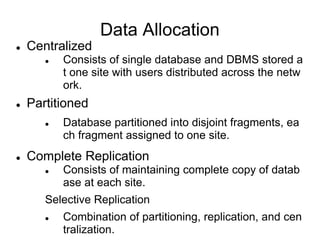
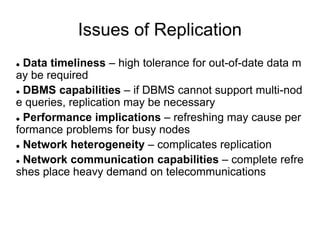
A distributed database is a collection of logically related databases distributed across a computer network. It is managed by a distributed database management system (D-DBMS) that makes the distribution transparent to users. There are two main types - homogeneous, where all sites have identical software and cooperate, and heterogeneous, where sites may differ. Key design issues are data fragmentation, allocation, and replication. Data can be fragmented horizontally by row or vertically by column and allocated centrally, in partitions, or with full or selective replication for availability and performance.