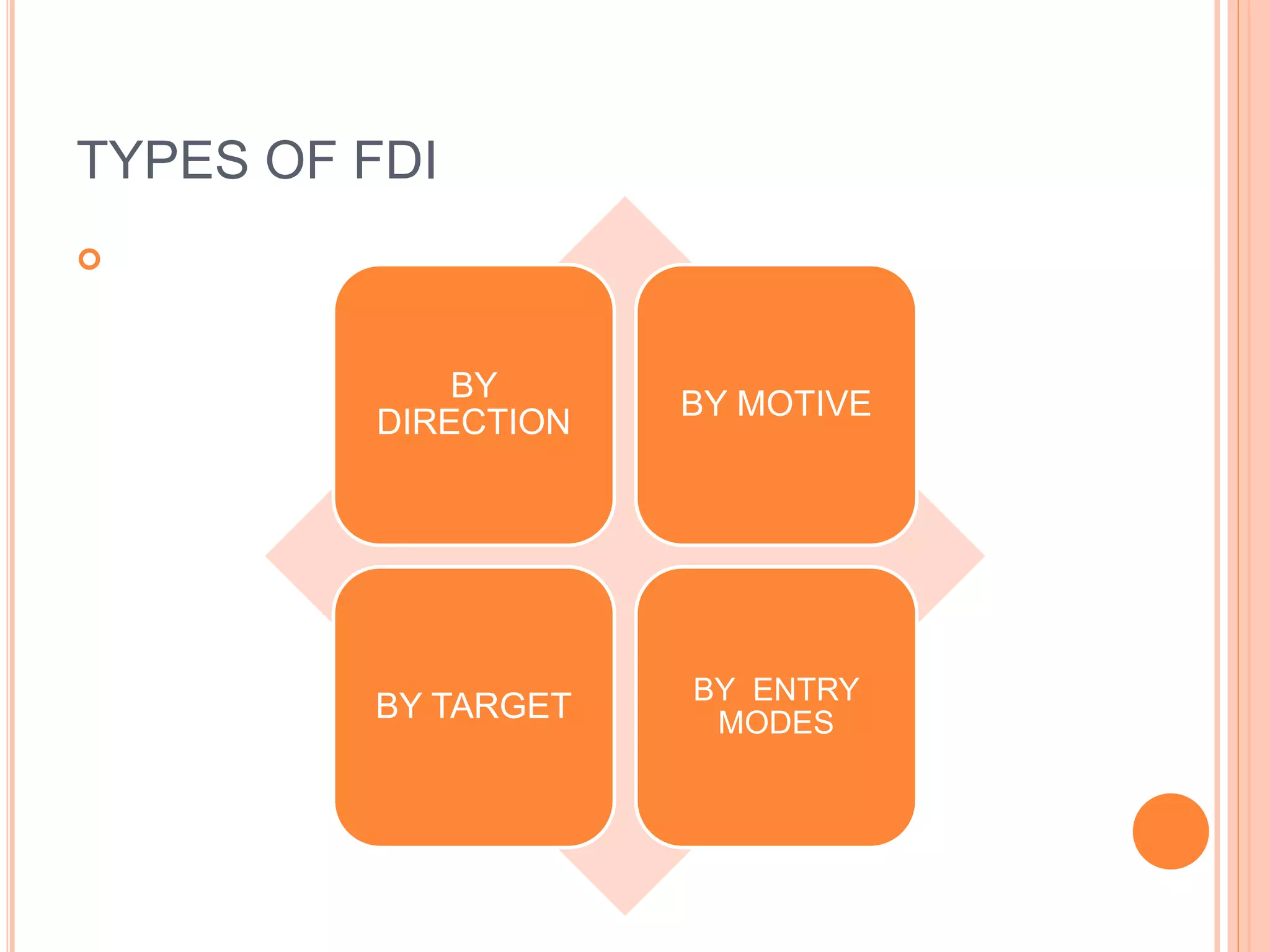
Foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to investment made by a company or entity located in one country into business interests located in another country. There are several types of FDI including horizontal FDI where a company operates the same activities abroad as at home, and vertical FDI where different stages of production are located in different countries. FDI can be motivated by seeking resources, markets, efficiencies, or strategic assets. It provides benefits like job creation and technology transfer but may also displace domestic companies. India allows FDI through an automatic route without approval for some sectors, and through a government approval process for other sectors regulated for national interest.