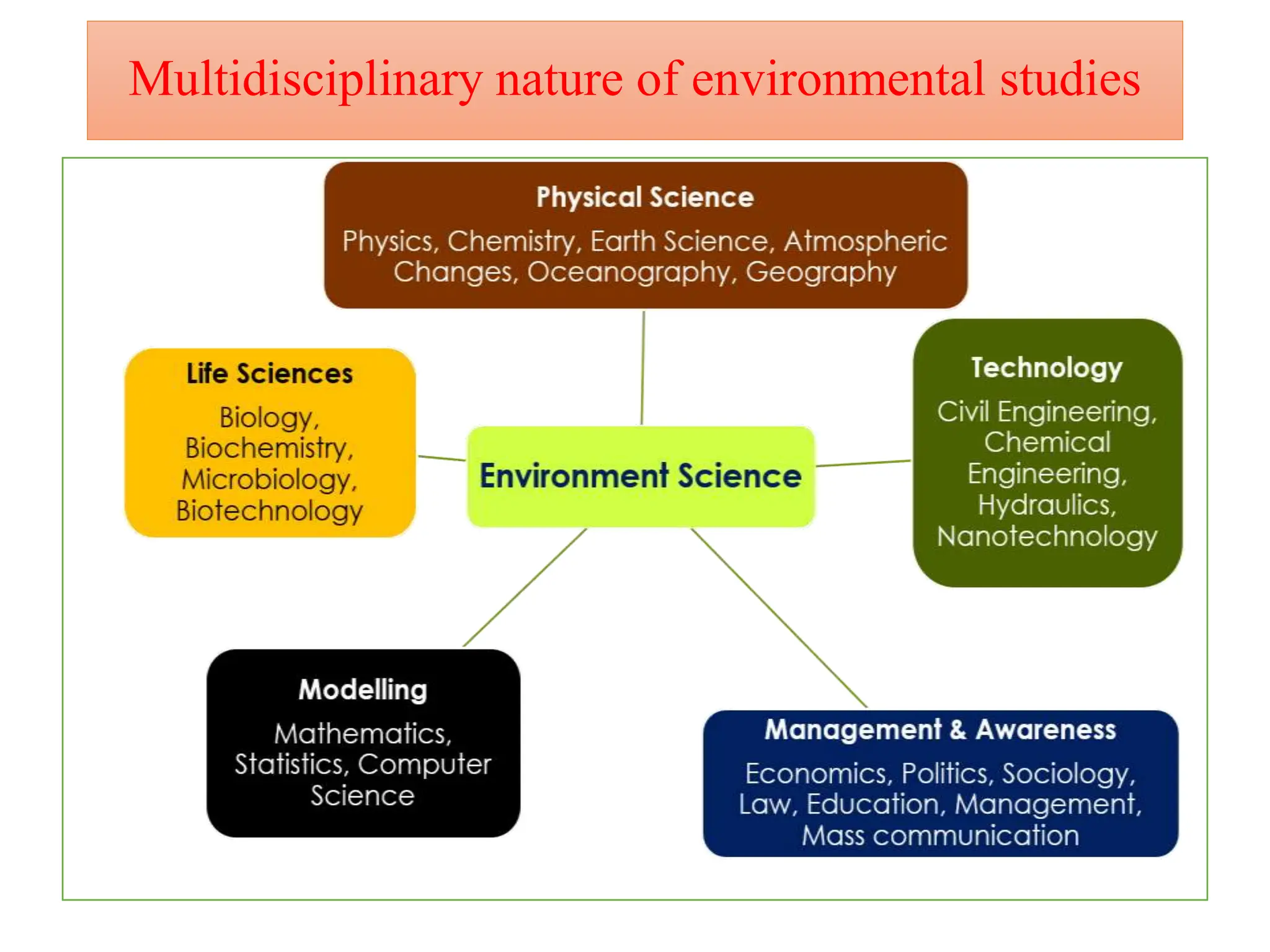
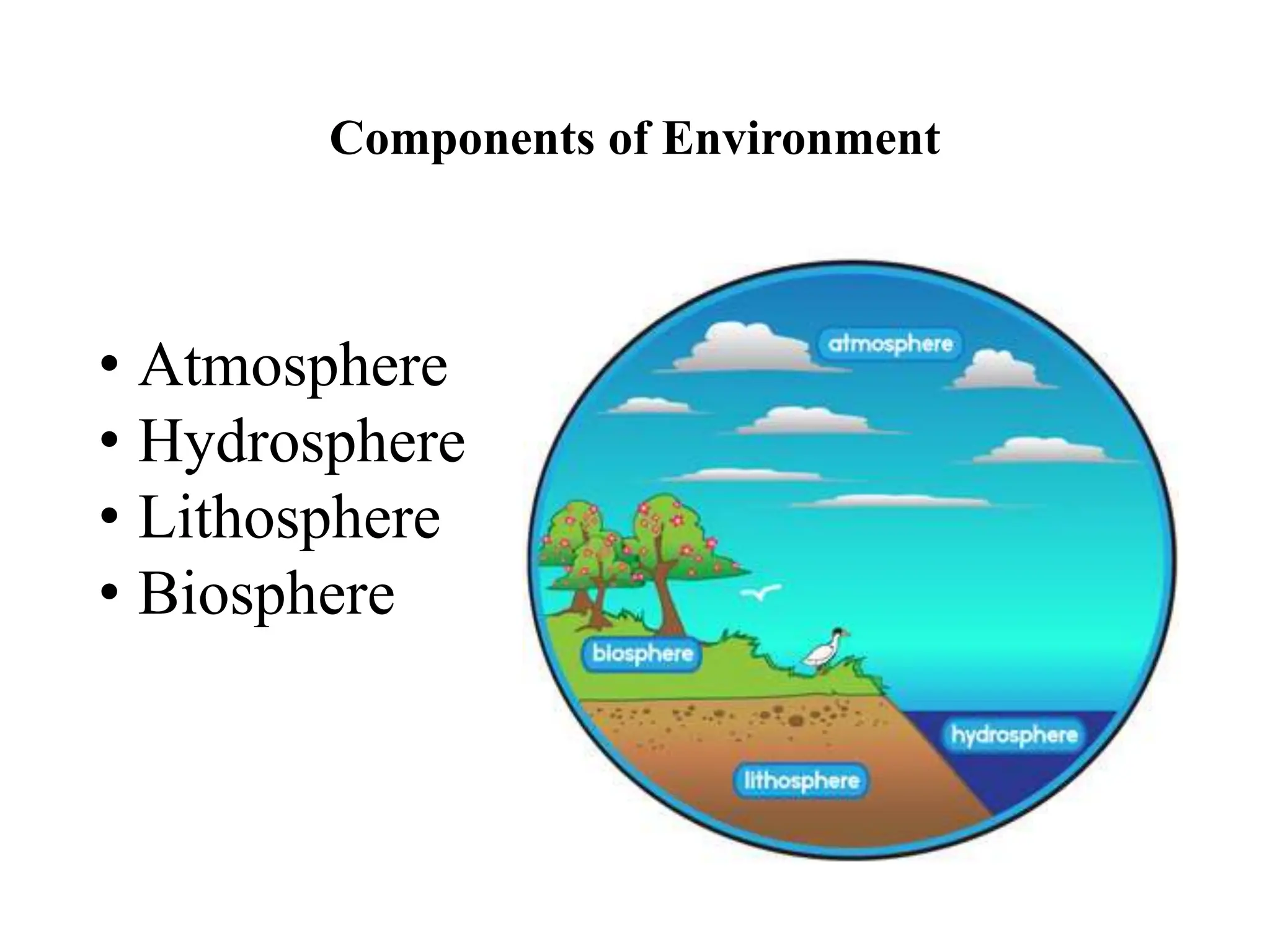
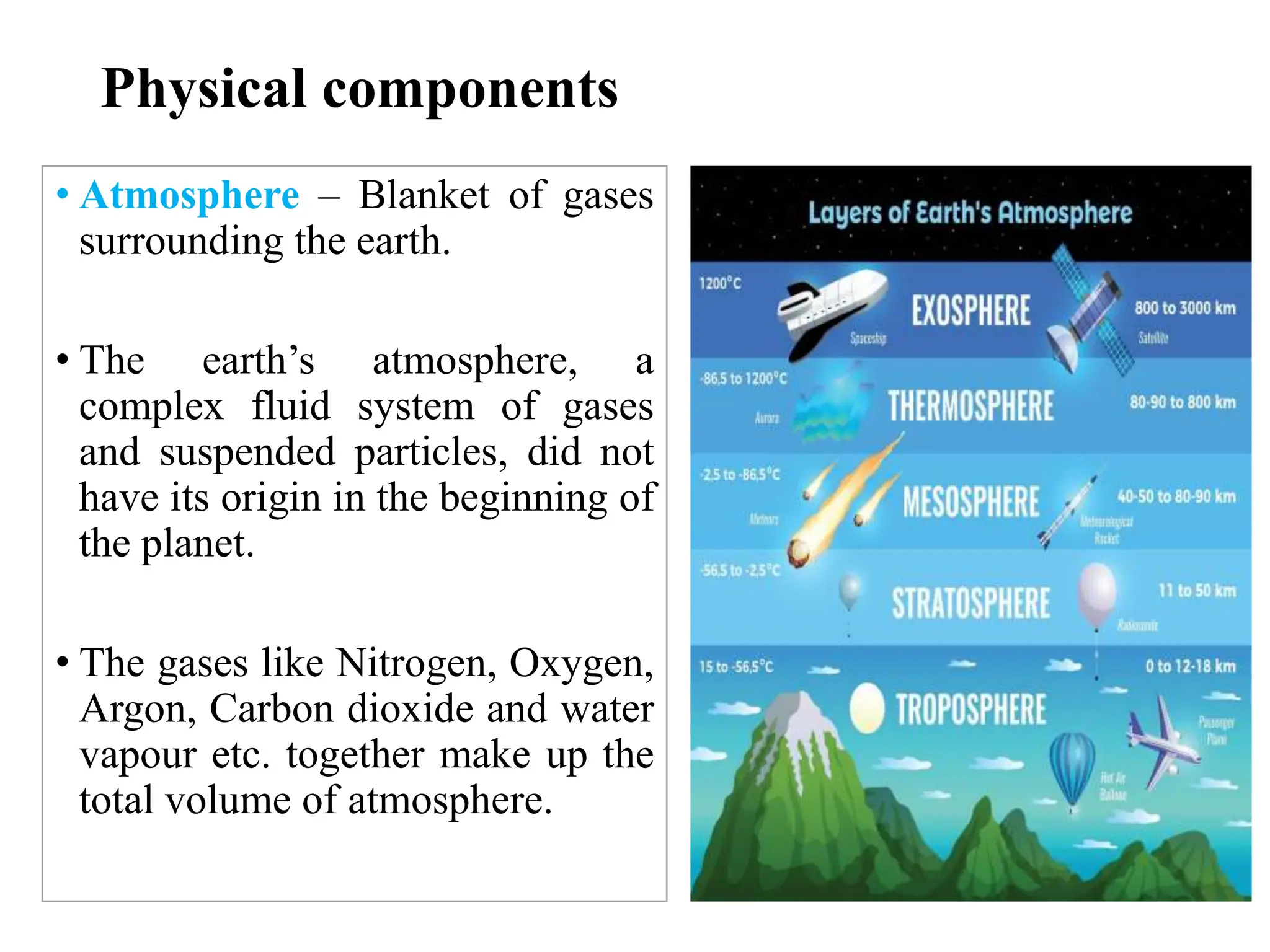
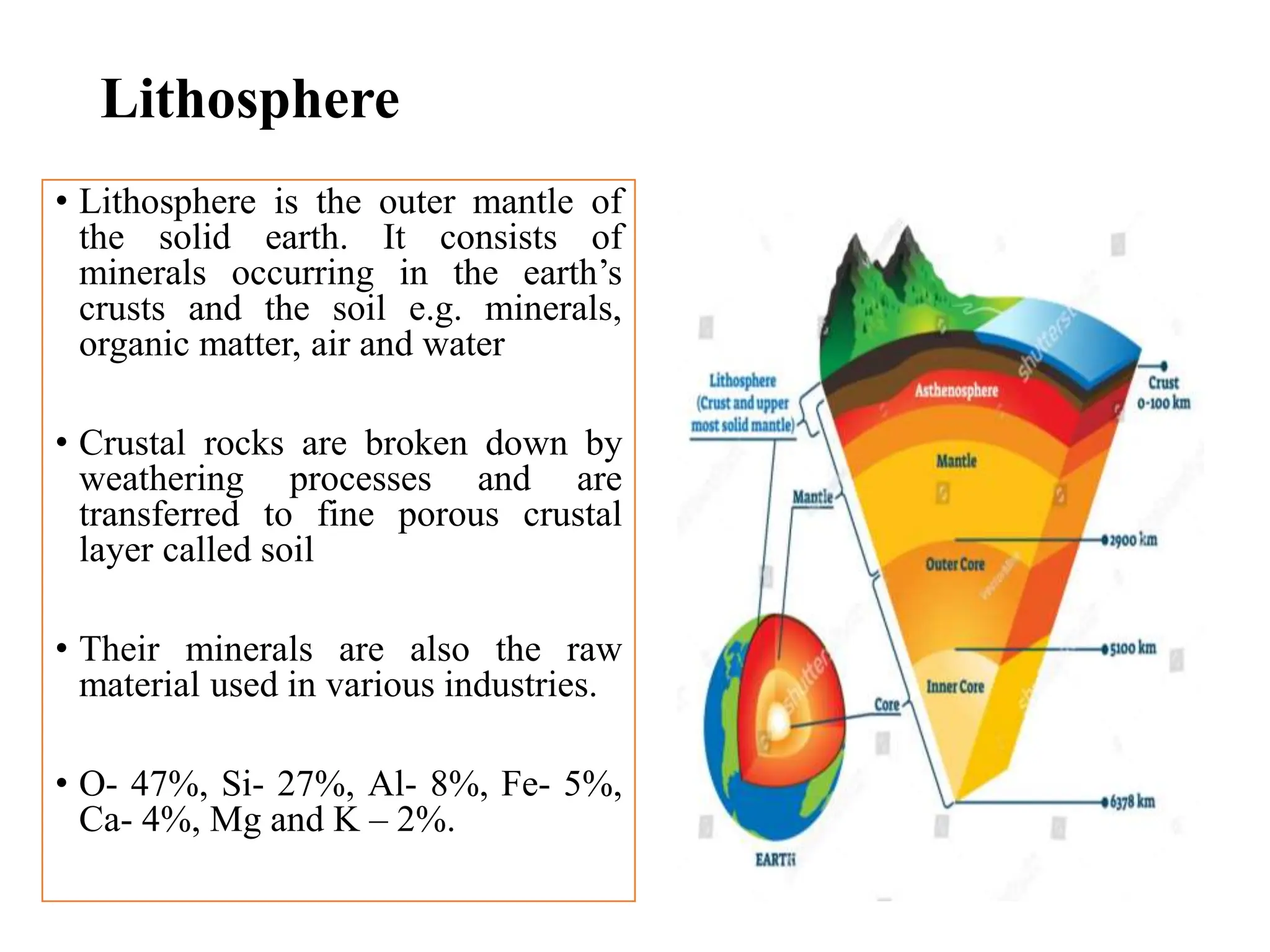
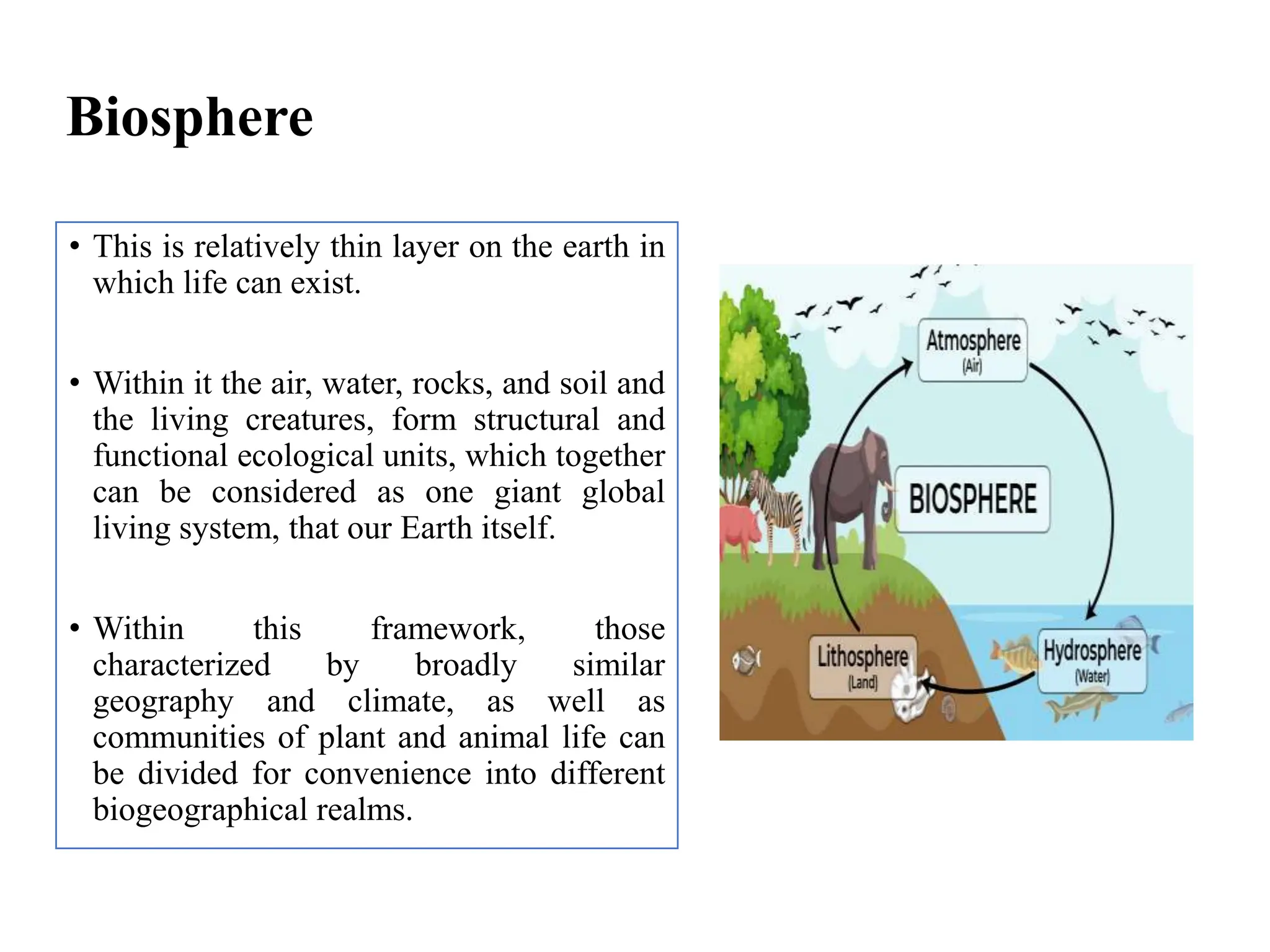
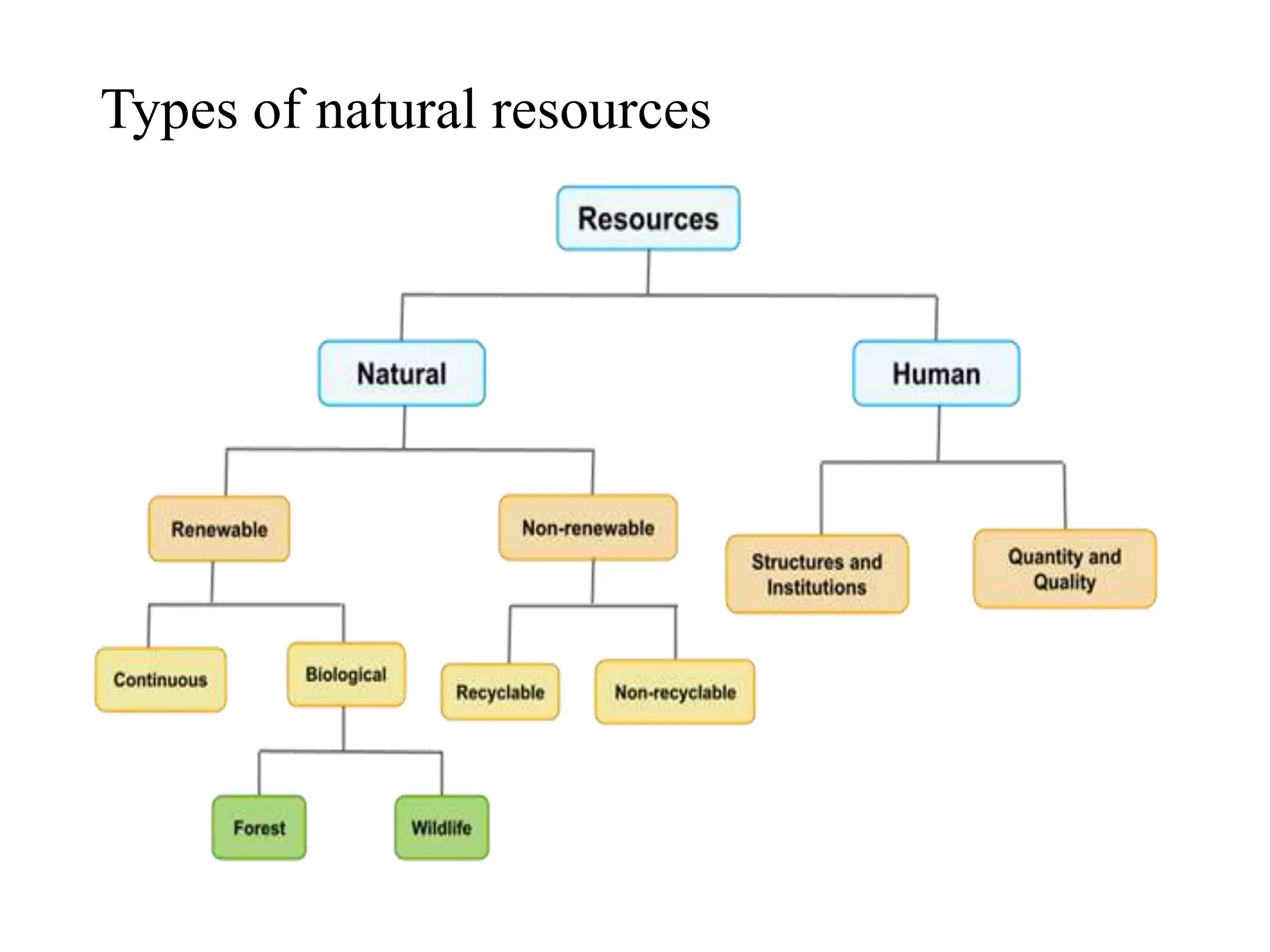
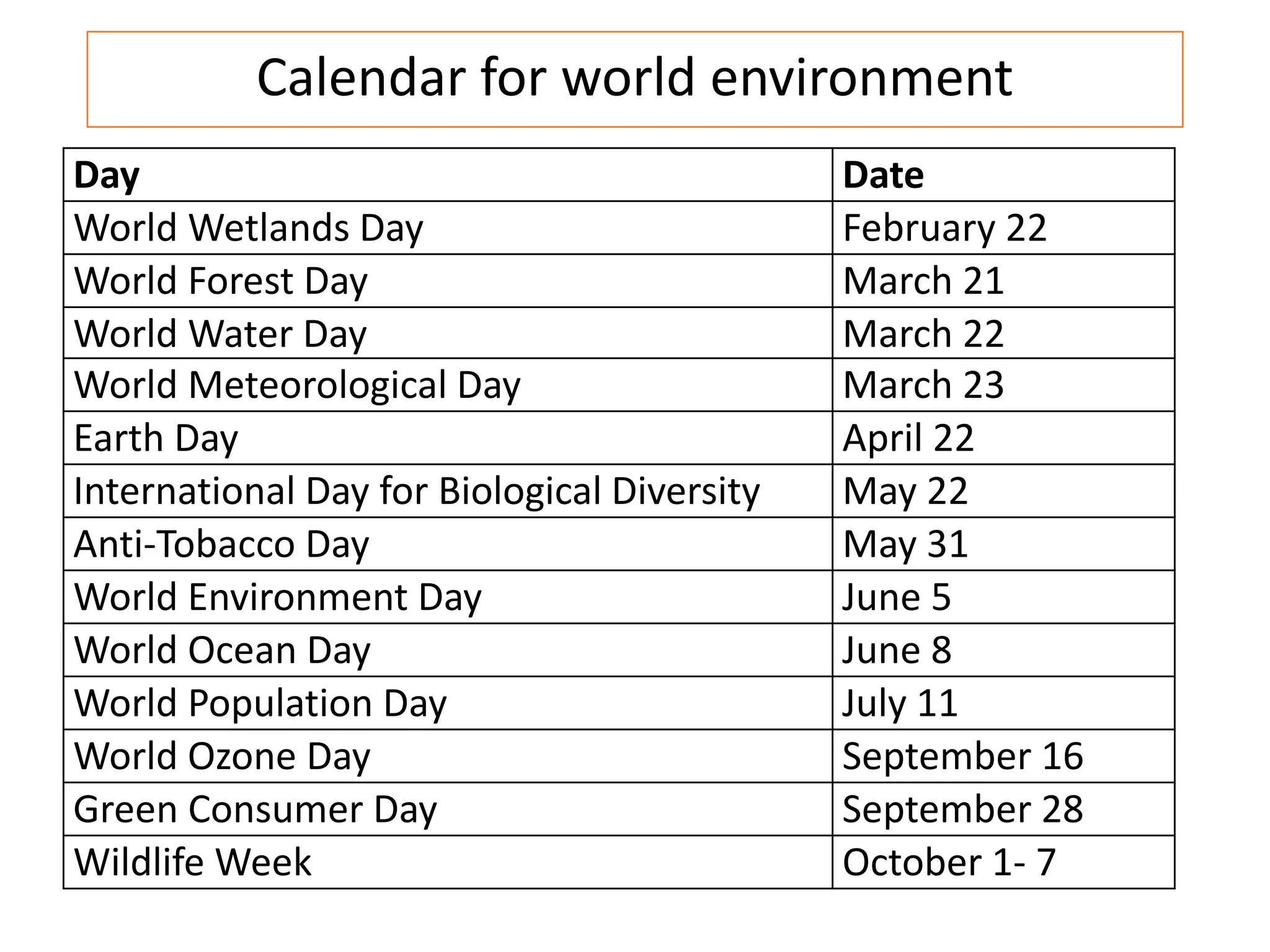
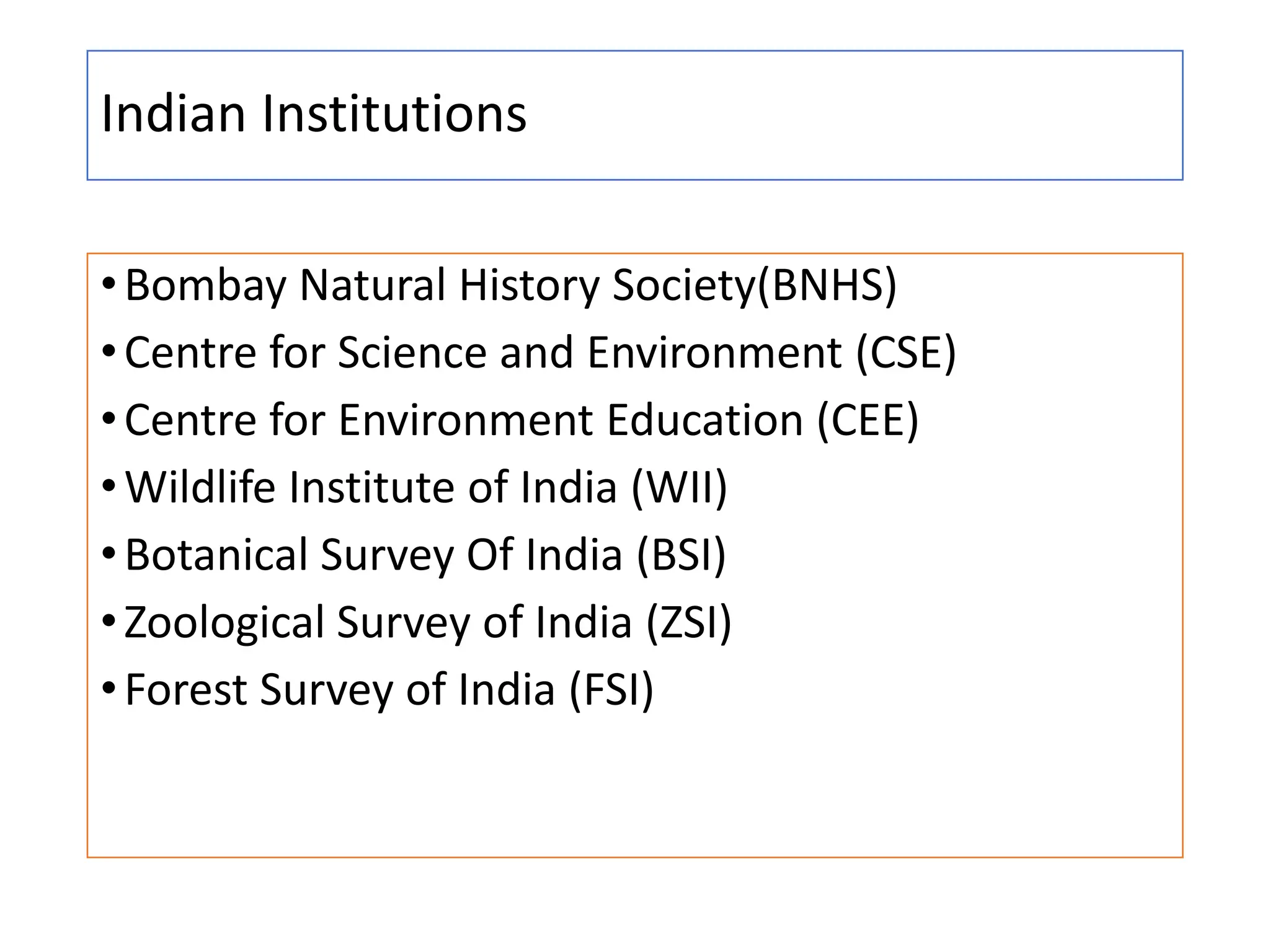
The document outlines the multidisciplinary nature of environmental studies, its definition, scope, and importance, emphasizing the interconnections between natural resources, ecology, and human impacts. It covers various aspects such as resource management, pollution control, social issues, and emerging career opportunities in environmental science and advocacy. Additionally, it discusses components of the environment, types of natural resources, and provides a calendar of significant environmental observances.